What Colors Make Green? – Complete Guide with Mixing Recipes
Are you beginning to explore color mixing? One of the first important aspects of this journey is to know how to mix your colors properly. With this in mind, the color green is one of the most complex colors to create, and there are plenty of variations to consider. You may think mixing green is a simple process, you take some yellow and mix it with some blue and you have green. However, in reality, it is not so easy. In this article, we will be showing you, in detail, the whole process of what colors make green and the various shades and tints.
How to Mix Green Colors?
There are basically three methods on how to mix green shades:
Mixing Primary Colors: To mix green, blend blue and yellow, the primary colors that when combined yield the secondary color green. Adjusting the ratio of blue to yellow will result in different shades of green, from pale lime to deep forest green.
Mixing Black with Yellow: Although not a standard method, adding a small amount of black to yellow can produce a greenish hue, but this tends to yield a darker, more muted green, often resembling an olive tone.

Each of these methods can be used to achieve various shades and tones of green, depending on the starting colors and the proportions used in the mix
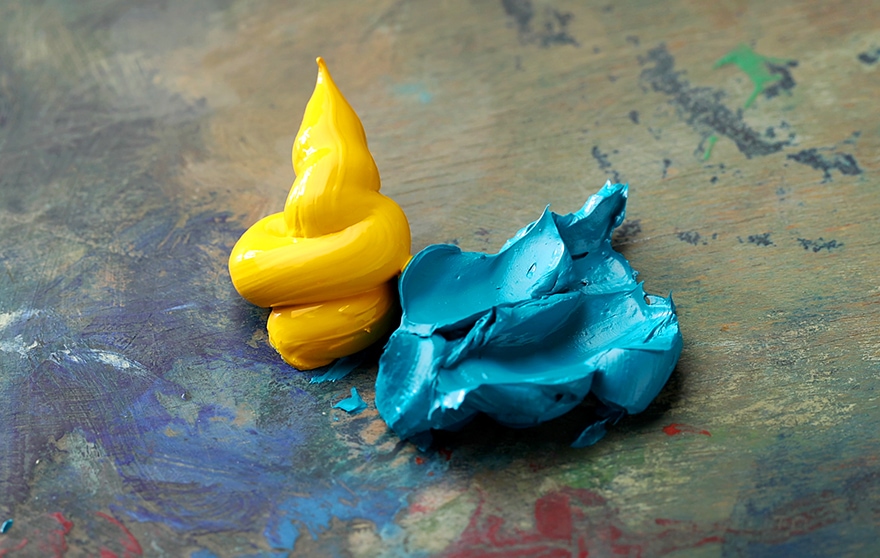

Take, for example, cadmium yellow that tends to lean towards red or a warmer color, whereas cadmium lemon leans more towards the cooler color of blue. When looking at the blue spectrum, for example, ultramarine blue tends to lean towards red tones, but manganese blue tends to lean more towards yellow tones.
Mixing Recipes for 25 Popular Color Shades of Green
| Shade Name | Mixing Recipe |
|---|---|
| Emerald | 2 parts Phthalo Green, 1 part Lemon Yellow |
| Green Yellow | 1 part Lemon Yellow, 1 part Phthalo Green |
| Chartreuse | 2 parts Lemon Yellow, 1 part Phthalo Green |
| Lime | 1 part Lemon Yellow, <1 part Phthalo Green |
| Lime Green | 1 part Lemon Yellow, 1 part Sap Green |
| Medium Sea Green | 2 parts Sap Green, <1 part Cobalt Blue |
| Forest Green | 1 part Phthalo Green, <1 part Burnt Sienna |
| Dark Cyan | 1 part Phthalo Green, 1 part Prussian Blue |
| Dark Green | 2 parts Phthalo Green, 1 part Ivory Black |
| Yellow Green | 2 parts Lemon Yellow, 1 part Sap Green |
| Olive Drab | 1 part Sap Green, 1 part Yellow Ochre, <1 part Burnt Umber |
| Olive | 1 part Sap Green, 1 part Yellow Ochre |
| Sea Green | 1 part Sap Green, <1 part Cerulean Blue |
| Medium Aquamarine | 1 part Sap Green, 1 part Titanium White, <1 part Cerulean Blue |
| Dark Sea Green | 1 part Sap Green, 2 parts Titanium White |
| Light Sea Green | 1 part Phthalo Green, <1 part Cerulean Blue, <1 part White |
| Pale Green | 1 part Sap Green, 3 parts Titanium White |
| Spring Green | 1 part Lemon Yellow, 1 part Phthalo Green, <1 part White |
| Dark Slate Grey | 1 part Phthalo Green, <1 part Ivory Black |
| Medium Spring Green | 2 parts Lemon Yellow, 1 part Phthalo Green, <1 part White |
| Light Green | 1 part Sap Green, 2 parts Lemon Yellow, 2 parts White |
| Medium Sea Green | 1 part Sap Green, <1 part Cerulean Blue |
| Saddle Brown | 1 part Burnt Umber, <1 part Cadmium Red, <1 part Phthalo Green |
| Olive | 1 part Yellow Ochre, <1 part Phthalo Green |
| Olive Drab | 1 part Sap Green, 1 part Yellow Ochre, <1 part Burnt Umber |
Examining the Color Bias
The above-mentioned trend or fact of mixing different shades of colors is referred to as a color bias, and you need to understand this as it will influence how you mix colors and will determine how accurate you can get to a specific color hue.
When Mixing Cool Primary Colors with Warm Colors
The art of mixing colors is, therefore, not as simple as just blending your primary colors. If you were to take stock of all the different shades of blue and yellow, you would be surprised at how many different shades of each color you can get. We know that by taking yellow and mixing it with blue we create green, but we now need to consider what shade of green we want to create.
A vibrant secondary green color can be created by mixing both the blue and yellow primary colors. If you take all three primary colors and mix them, you will end up with a secondary color that is slightly muddy and resembles more of a brown. This can be seen when you mix blue that has a warmer hue with yellow that also contains red, you will then accidentally be mixing all of the three primary colors.
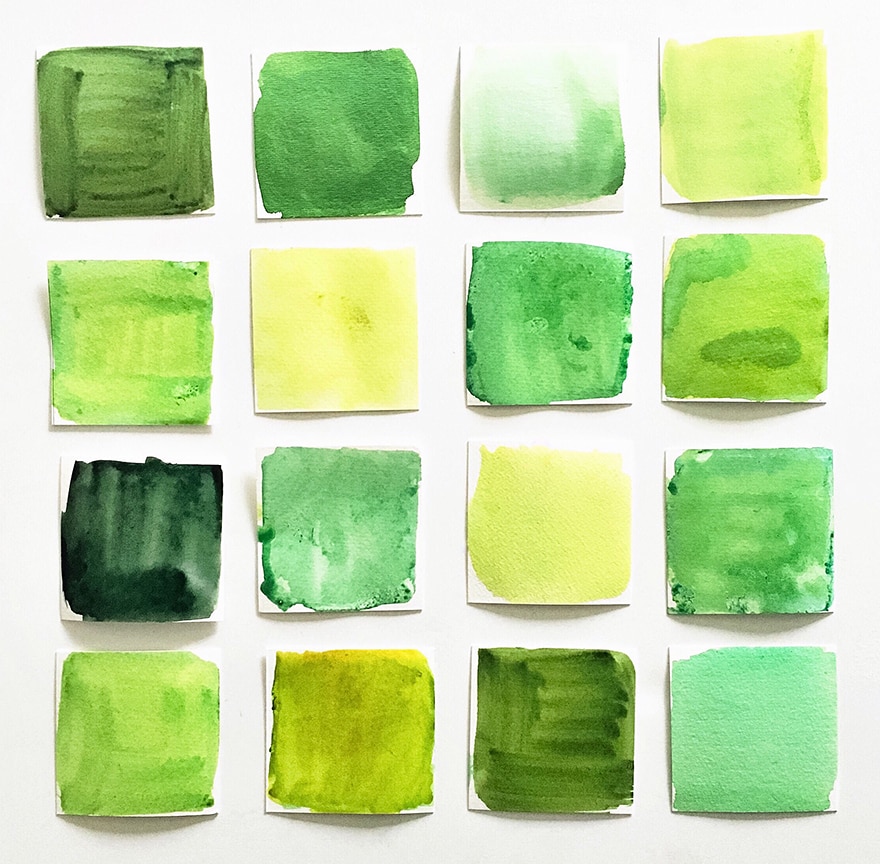

Classifying Yellows from a Cool to a Warm Color
You can distinguish the relative temperature of a yellow color just by looking at it. This means that a shade of yellow that leans more towards orange is warmer than other yellows that show more green color. It is our opinion that color temperatures should be seriously considered and not just glossed over. The color classifications we are discussing here are based on oil paint names. The yellow color classification from cool to warm is as seen below:
- Light Cadmium yellow or Cadmium lemon
- Cadmium yellow
- Naples yellow
- Yellow ochre
Classifying Blues from a Cool to a Warm Color
The exact shade of green can be altered by changing the shade of blue or yellow you are using. The same as yellow colors, blue colors also vary from cool to warm so there are many blue tones available. The blue color classification from cool to warm is as seen below:
- Manganese blue
- Cobalt blue
- Ultramarine blue
Softening Bright Green Colors with Complementary Colors
Mixing a cool yellow with a cool blue produces a bright, vibrant green suitable for painting scenes with natural elements. However, to achieve more realistic and varied green shades, it’s essential to learn how to soften the green by adding a small amount of a complementary red color. Doing so reduces the vibrancy of the green.
It’s important to note that different shades of red will affect the green differently. For example, alizarin crimson can soften green while maintaining its coolness. In contrast, for an earthier and darker green, mixing in a warm red like burnt sienna is recommended. Understanding the color wheel is beneficial for effectively mixing and achieving the desired green shades.

Regulating the Temperature of Your Green
When we are looking at regulating your color temperature, you should think about how to create cool and warm shades of green. As we have seen in this article, color temperature is vital when you start mixing any color, but especially for green shades. If you are painting a nature scene, you want to use different temperatures to be able to depict a bright and sunny day or a cold and wintery afternoon. Next, we will be using, purely as an example, a green that is a mixture of cadmium yellow and ultramarine blue.
Making Cooler Shades of Green
To create cooler shades of green, you can incorporate purple hues or select cool shades of green. Adding a cool blue can further chill the green tone, but it’s important to choose a blue with cool undertones. For emerald green, specific mixing methods can be applied.
Using purple to cool green:
- Dioxazine Purple: A darker purple that cools and darkens green simultaneously.
- Provence Violet Bluish: Lightens the green without darkening it, resulting in a subtle cool green.
Using green tones to cool green:
- Veronese Green: A teal-like cool green that enhances saturation, making the green more vibrant.
- Pthalo Green: Intensely cools and saturates green, and can also darken the shade if desired.
These methods offer various outcomes, from dark and cool to vibrant and saturated greens, providing flexibility in achieving the desired cool green effect.

Making Warmer Shades of Green
You should by now be aware that if you add warm colors like yellows, oranges, and reds, it will have the effect of warming your green. By using cadmium orange, for example, has the amazing effect of warming your green. If you are looking for an earthy green, yellow ochre will warm up your green tone. Remember, that because yellow ochre is earthy in color, you will land up with a green that is a little more towards the brown side.
Another amazing option if you want to warm up your green tone is to make use of a small amount of Alizarin crimson. The pigment of this color is very dark so you will come out with a darker shade of green. If you want the best results for warming your green tone, then the best red color to use is cadmium red.

Shading and Tinting: How to Create Different Levels of Green?
If you want answers to the questions like how to make olive green paint, what two colors make dark green, or what colors make light green, then read on. When making colors darker, you should work with shades or work with tints for lighter colors. Because green is a secondary color, trying to get the correct shade of green requires plenty of considerations. This why tinting and shading can be a slightly complicated process.
NOTE: Normally you would use white, which is the tint most commonly used when making colors lighter. However, when dealing with green, white is not the best option to use. When you add white to your green tone, you come out with a shade that looks like sage green that lacks depth.
When you are shading your colors, the most common color to use is black, as many black paints contain a green base. The green base can be a problem if you want to create a grey color, but it is the perfect answer for shading green. If you are interested to know how to make forest green, it is very simple. Simply add a small amount of black. However, if you want to create darker shades of green, then you will have to spend some time experimenting.
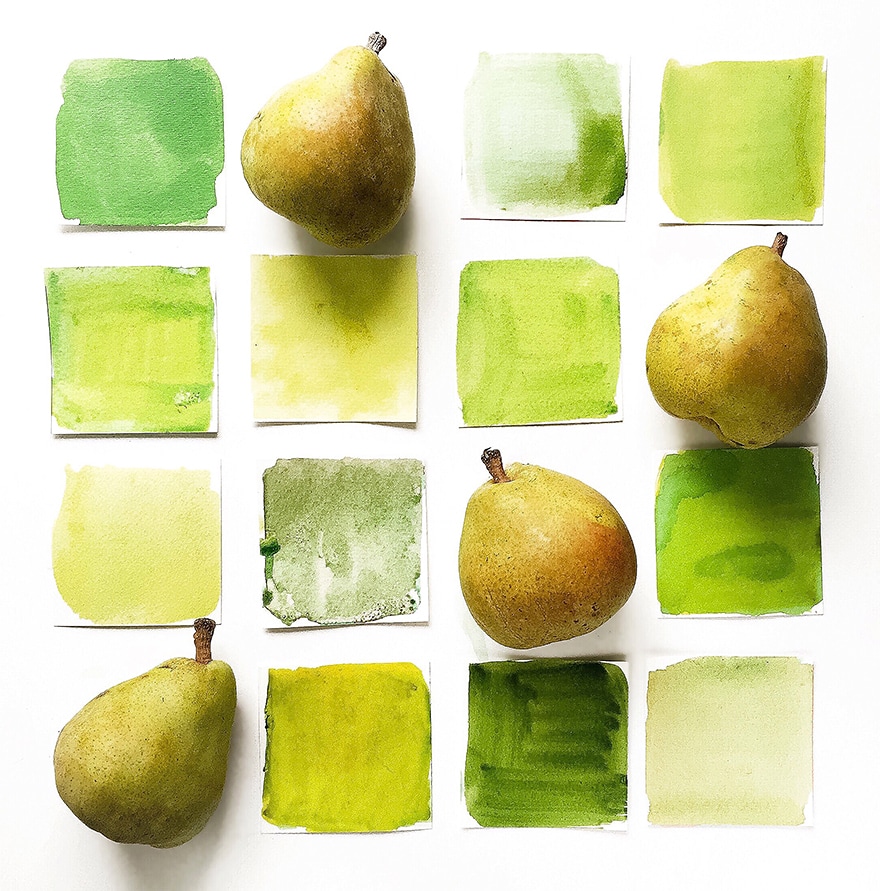

Creating Lighter Tints of Green
Whenever you are painting and using green, light green shades form a vital part of your painting project. When you need to create color variations of leaves, or if you want to highlight the area where the sunlight strikes a green surface, then you need to know and understand how to create lighter tints of green. If you are interested in knowing what colors make mint green, use a beautiful shade of green and add a small amount of white?
NOTE: If you are interested in knowing what colors make light green, you first need to take into account a few things. By adding white to your green tone is the simplest method to use when making light green. However, why limit yourself to this single option, as there are many other methods available to give you even better results. Creating light green by using white will give you an uninspiring and pale green tone.
Lightening Your Green by Using Yellow
By adding a small extra amount of yellow to your green tone, will give you an amazing light green shade. So, by using different yellows in varying amounts, you will be able to create numerous light green shades. The yellow will not only make the green light but will also give it a far more vivid color. If you are interested in knowing what colors make mint green, simply take your green tone that consists of a reasonable amount of yellow and then add a small amount of white.
To create lime green shades, just add a small amount of cadmium light yellow. If you want your green shade to be warmer and lighter, just add a warmer yellow color. When mixing any type of substance, you need to experiment a little and the same applies to mixing paint colors.

Dark Shades of Green
Understanding what two colors make dark green shades is just as vital as understanding what colors make light green. If you want to emphasize certain dimensions by adding shadows or create variations, darker shades of green play an important part in your painting project. You need to understand what two colors make dark green.
There are so many instances where you will need to make use of a variety of rich dark green tones. By using black, is the quickest and easiest way to give your green a darker color. However, similar to making your green lighter, using only this one method may result in your painting turning out monotone and dull.
How to Darken Your Green by Using Purple or Other Colors?
To create a rich and deep dark green shade a fantastic option is to add a small amount of purple. Because purple is a secondary color, it does contain some red, so you will need to mix an earthy darker green tone to form a darker green shade. However, if you want a slightly lighter and warmer green tone, add some Dioxazine purple as it is a much cooler purple shade.
You can also get a darker green shade by adding a small amount of Pthalo green; this will give you a cooler dark green shade similar to dark teal. This particular green will make your green rapidly darker, so you should control the amount you add by only using small amounts. This is a very saturated color, so you will have to soften or dull it slightly by adding a small amount of Alizarin crimson. Experiment further by adding a small amount of dark blue paint with your green mix to get a cool darker green tone.

NOTE: To create an earthy dark green that resembles more of a brown, you can add some burnt umber to your green mix. The pigments of the burnt umber have a brown tone, and if you do not want an earthy green tone, then stay away from the option of burnt umber.
How to Create Green without Using Yellow
This almost seems like a contradiction to creating green by mixing yellow and blue. So, how is it possible to make green with no yellow? All the facts point towards yellow and blue making green. However, it is possible to make a range of green shades without making use of yellow, and you will be amazed as to the many available options.

Making Green by Using Orange
If you’re not using yellow to create green, you can mix orange with blue to achieve a range of green shades. A cool orange, which is closer to yellow, is recommended for these mixes. For a light green tone, blend cool orange with a cool blue like Phthalo blue, adjusting the proportions as needed to get a bright light green.
For a more subdued, earthy green, mix the orange with Ultramarine blue. To achieve a darker green with brownish tones, combine orange with black or grey. Each blue will interact with the orange differently, so experimentation is key to achieving the desired shade of green.
Making Green by Using Raw Sienna
Similarly, you can also make green by using raw sienna. Here you will find that these types of green shades will not be as bright and vivid as when you use yellow because raw sienna is a lot warmer color. We suggest you try and experiment a little by mixing raw sienna with a variety of blue colors to see what shades of green you can create. By mixing raw sienna with Pthalo blue, will give you a beautiful deep blueish-green color. When mixing raw sienna with Prussian blue, you will create more of an earthy green shade.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do You Make Light Green Color?
You can create a bright vibrant light green tone when you mix a large amount of light yellow with a small amount of blue. Do you want to know how to make mint green paint, simply add a small amount of white to your light green? If you want to make your green shade lighter, just add a small amount of white or yellow.
How to Make Forest Green Paint?
This is fairly easy, take any green shade and mix it with blue or yellow. If you want to make your green tone darker, just add a small amount of black, or you can also add a small amount of purple for the same result.
Is it Possible to Create Green with no Yellow?
It is possible to create a large range of green shades without making use of yellow. You can use a bright and cool orange shade to replace the yellow tone when creating your green shade. If you have a color mixing chart available, it will help you to see what blue and cool orange tones to use.
In 2005, Charlene completed her Wellness Diplomas in Therapeutic Aromatherapy and Reflexology from the International School of Reflexology and Meridian Therapy. She worked for a company offering corporate wellness programs for a couple of years, before opening up her own therapy practice. It was in 2015 that a friend, who was a digital marketer, asked her to join her company as a content creator, and this is where she found her excitement for writing.
Since joining the content writing world, she has gained a lot of experience over the years writing on a diverse selection of topics, from beauty, health, wellness, travel, and more. Due to various circumstances, she had to close her therapy practice and is now a full-time freelance writer. Being a creative person, she could not pass up the opportunity to contribute to the Art in Context team, where is was in her element, writing about a variety of art and craft topics. Contributing articles for over three years now, her knowledge in this area has grown, and she has gotten to explore her creativity and improve her research and writing skills.
Charlene Lewis has been working for artincontext.org since the relaunch in 2020. She is an experienced writer and mainly focuses on the topics of color theory, painting and drawing.
Learn more about Charlene Lewis and the Art in Context Team.
Cite this Article
Charlene, Lewis, “What Colors Make Green? – Complete Guide with Mixing Recipes.” Art in Context. March 12, 2021. URL: https://artincontext.org/what-colors-make-green/
Lewis, C. (2021, 12 March). What Colors Make Green? – Complete Guide with Mixing Recipes. Art in Context. https://artincontext.org/what-colors-make-green/
Lewis, Charlene. “What Colors Make Green? – Complete Guide with Mixing Recipes.” Art in Context, March 12, 2021. https://artincontext.org/what-colors-make-green/.









