Analogous Colors – What Are Analogous Colors in Color Theory
There is always more to creating great designs than meets the eye. Many do not realize the importance color plays in everyday designs online and at home. Colors have a profound effect on our lives, even if we do not notice them at first, but how do designers know what colors to use? The whole process has to begin with understanding color theory and how colors are connected. So, what are analogous colors and how do they work?
A Brief Look at Color Theory
At school, we all learned about the basics when it came to colors, so most of us know what primary, secondary and tertiary colors are. Color theory takes these colors further and places them in a visual representation known as the color wheel. Today, you can get more than one color model that is based on traditional or modern ideas.
Traditional and Modern Color Wheels
The traditional color wheel is based on what we learned at school and is known as the RYB color model. In this color system, the primary colors are red, yellow, and blue, which you can then combine to make your secondary colors orange, green as well as purple. Then you also have your intermediate or tertiary colors including blue-green, yellow-green, red-purple, blue-purple, yellow-orange, and red-orange. These colors are created when paint pigments are mixed.
The modern color wheel is based on how light combines to create various colors and is used by graphic artists or web designers and is how your television and computer screens work.
This color model uses the RGB color codes, which represent red, green, and blue. When searching for specific colors online, each color has a hex code that identifies it and a breakdown of how much of each color is present. You might also notice another color code with the letters CMYK. This is used for printing purposes and will you how much of each ink color is used to produce a specific color. The primary colors involved here include cyan, magenta, yellow, and lastly, black.
How to Determine the Different Color Combinations
Color theory and the color wheel is what can help determine the best color combinations. Graphic artists and other designers use this to create appealing designs that work. The basic idea is that all the colors have their place on the color wheel, and how they are positioned and relate to one another is how to determine different color combinations. There are more color combinations besides analogous and these include the following.
- Complementary colors: Contrasting colors or colors that work well and stand out are complementary. These are found on opposing ends of the color wheel.
- Monochromatic colors: These colors are obtained from a single color, and use various tones, tints, and shades.
- Triadic Colors: These three colors also form a contrast and go nicely together, and on the color wheel, they form a triangle with equal sides.
- Tetradic colors: These, as well as the square color combinations, use four colors. The tetradic colors form a rectangle and have multiple sets of complementary colors.

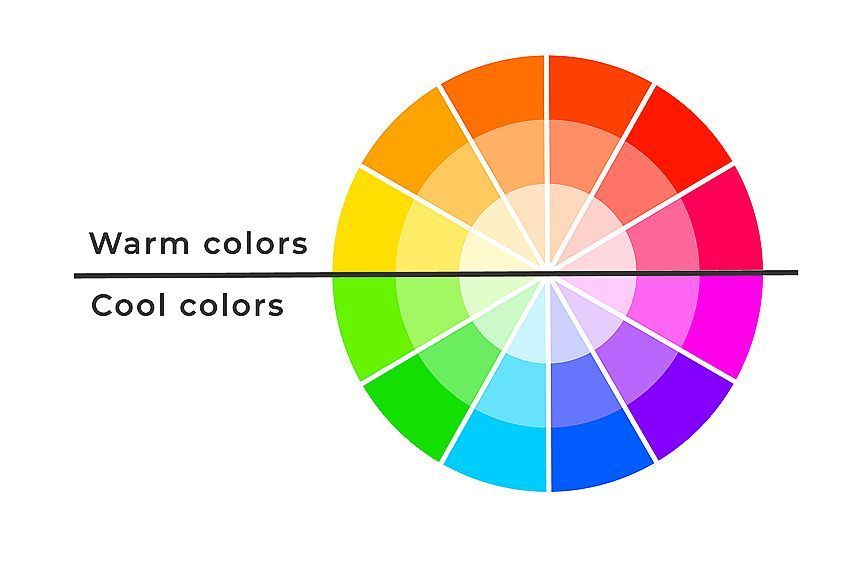
Besides the main colors in a color wheel, it also contains various shades, tints, tones, and hues, which increases your choice of colors exponentially. You can also see the color temperature, which means all the cooler colors like blue, and green are found on one half of the color wheel, while warmer colors like red, orange, and yellow are found on the other half.
- Hue: This is another term you can use for color.
- Shade: A shade is a color to which black has been added to darken it.
- Tint: A tint is a hue that white has been added to, so it becomes lighter.
- Tone: Colors with a similar hue and lightness but have a different saturation.
- Saturation: The saturation is an indication of the purity or intensity of a color.
What Are Analogous Colors?
So, what are analogous colors? We have mentioned the other color combinations you can get, but our focus today is on analogous colors. In this color combination, there are usually three colors, which can all be found adjacent to one another. You will choose your main color and from there, you have your supporting and then your accent color.
These colors all share similar characteristics or traits and go well when used collectively. Analogous colors are harmonious and pleasant to look out for, without standing out as the complementary colors do. The word “analogous” actually refers to two things that have functions or features that are alike. Analogous and monochromatic colors are similar in this fashion.
For example, green and yellow are neighbors on the color wheel. These two colors combined form yellow-green, which has traits of both colors. All three colors are analogous, as they are all connected.
Examples of Analogous Colors
There are 12 basic analogous color combinations you can choose from. Each of these combinations has three colors and is located somewhere on the color wheel. Below is a list of these analogous colors.
- Red, red-orange, orange
- Yellow-orange, yellow, yellow-green
- Green, blue-green, blue
- Blue-violet, violet, red-violet
| Shade | Hex Code | CMYK Color Code (%) | RGB Color Code | Color |
| Red | #ff0000 | 0, 100, 100, 0 | 255, 0, 0 | |
| Red-Orange | #ff5349 | 0, 67, 71, 0 | 255, 83, 73 | |
| Orange | #ff8000 | 255, 128, 0 | 255, 128, 0 | |
| Yellow-Orange | #ffae42 | 0, 32, 74, 0 | 255, 174, 66 | |
| Yellow | #ffff00 | 0, 0, 100, 0 | 255, 255, 0 | |
| Yellow-Green | #9acd32 | 25, 0, 76, 20 | 154, 205, 50 | |
| Green | #00ff00 | 100, 0, 100, 0 | 0, 255, 0 | |
| Blue-Green | #0d98ba | 93, 18, 0, 27 | 13, 152, 186 | |
| Blue | #0000ff | 100, 100, 0, 0 | 0, 0, 255 | |
| Blue-Violet | #8a2be2 | 39, 81, 0, 11 | 138, 43, 226 | |
| Violet | #ee82ee | 0, 45, 0, 7 | 238, 130, 238 | |
| Red-Violet | #c71585 | 0, 89, 33, 22 | 199, 21, 133 |
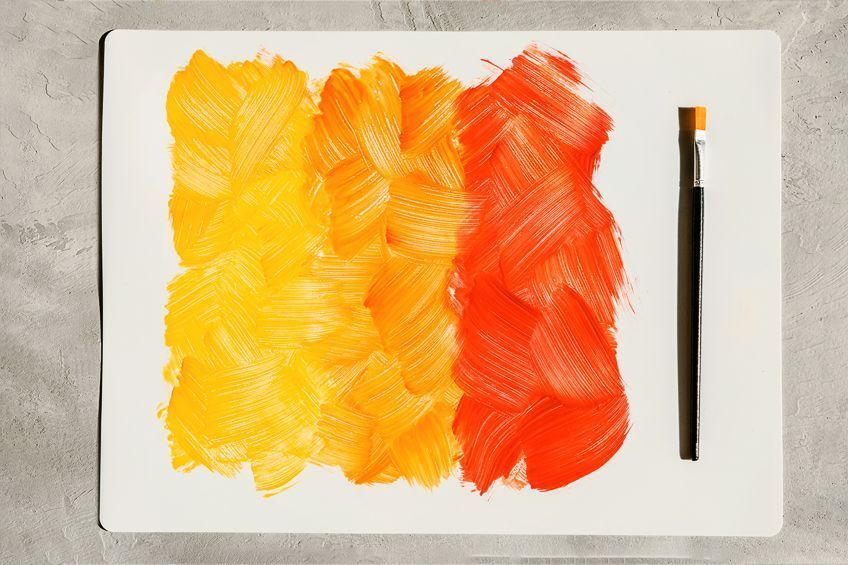

Analogous Color Combinations in Art and Nature
Analogous colors have been used in art to help express emotions, meaning, and tone. If used properly, the use of analogous colors can help to create something that is recognizable and connects with the viewer. For example, the well-known artist Claude Monet used analogous colors to create a piece that has energy in his Water Lily Pond (1899) painting. You can see he uses a green analogous color combination. Another example of yellow, orange, and yellow-orange would be the flowers in Vincent van Gogh’s Sunflowers (1888).
You can try to create analogous colors as well. Consider primary and secondary colors like green and blue.
With these colors, you can then mix green-blue, blue-green, and all colors in between. All of the colors will have something in common, and that is the color blue. Analogous colors abound in nature, which is where many artists get inspiration from. Many types of leaves display analogous color combinations, and you can see green, yellow, and yellow-green shades of color.
The Meaning Behind Analogous Colors
All colors have meaning and can affect how we feel, sometimes, even directly affecting our physical bodies. Analogous color schemes occur naturally and are pleasant to look at, which makes them a popular option in various designs.
Colors are used in advertisements, marketing, and even movies to bring about certain feelings and associations. Colors can be stimulating or calming, or they can be associated with nature or romance. Analogous colors, depending on the hue, can be used in all these cases. For example, green, yellow, and yellow-green can be connected to nature.
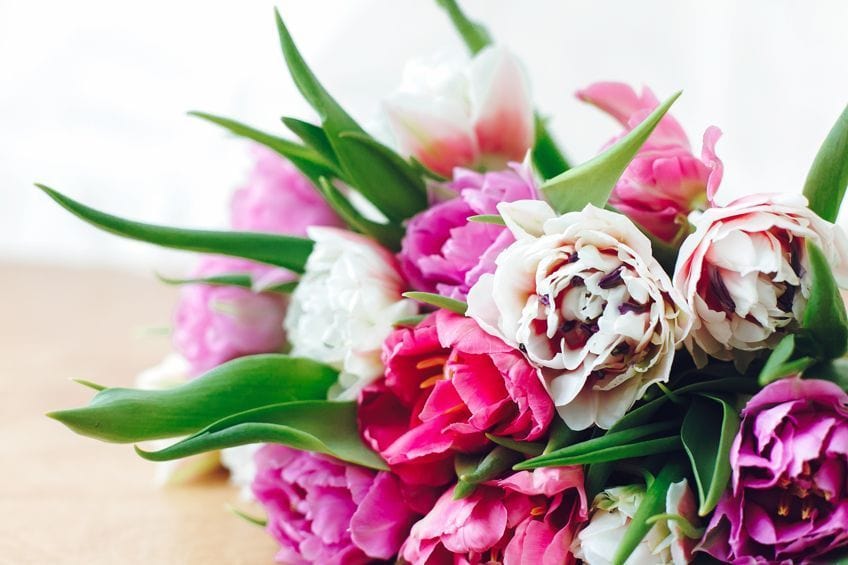

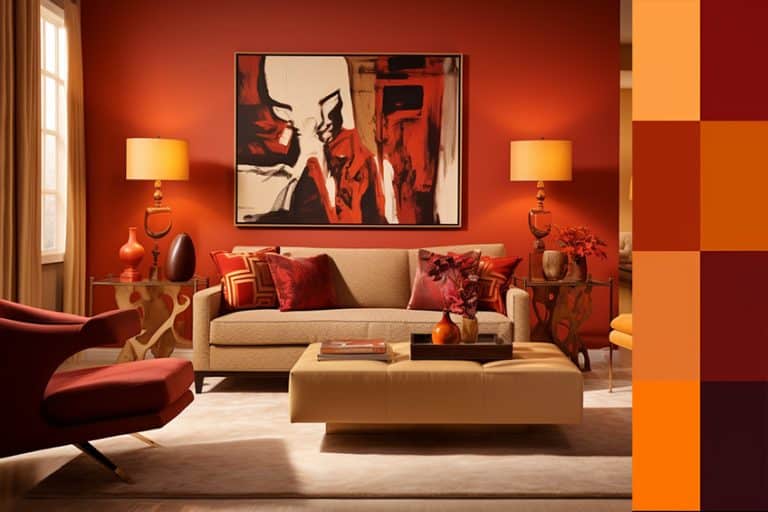
Many different emotions and experiences can be created by using analogous colors. Warmer analogous color schemes that contain red, red-orange, and orange can be more stimulating, while calmer combinations will include blue, blue-green, and green color schemes. Ultimately, the color scheme you choose will depend on what you want the outcome to be.
How to Use Analogous Colors
Analogous colors are used in all types of design ideas from graphic designs for websites, to advertising, marketing, interior design, movies, and more. Analogous colors can be used to create a harmonious and balanced color scheme that is clear, where colors work effortlessly together. Make sure to choose an analogous color scheme that has tonal contrast, to easily identify each color. You can also incorporate gray, black, and white into an analogous color theme.
You can go about choosing color combinations yourself, using the color wheel, or you can use the many tools and websites available. Simply choose your main color, which should have its own hex code that identifies it, and with this, you can determine all the best color combinations.
A design is dependent on the message you want to send or the feeling you wish to create, which makes it a subjective decision.
However, for example, if you wish to use a red, red-orange, and orange combination, consider selecting the red-orange color as your main attraction, and use the other two as accents. Choosing the middle color can help to produce a more balanced look.
When you want to go for a more energetic look, you may want to consider contrasting colors or complementary colors instead. Analogous colors tend to be more harmonizing and calming in nature. A business that can take advantage of an analogous color scheme is a wellness spa or other natural products. The sense of calm and balance should work perfectly with analogous colors. Analogous colors are also ideal for bedroom designs in the home.
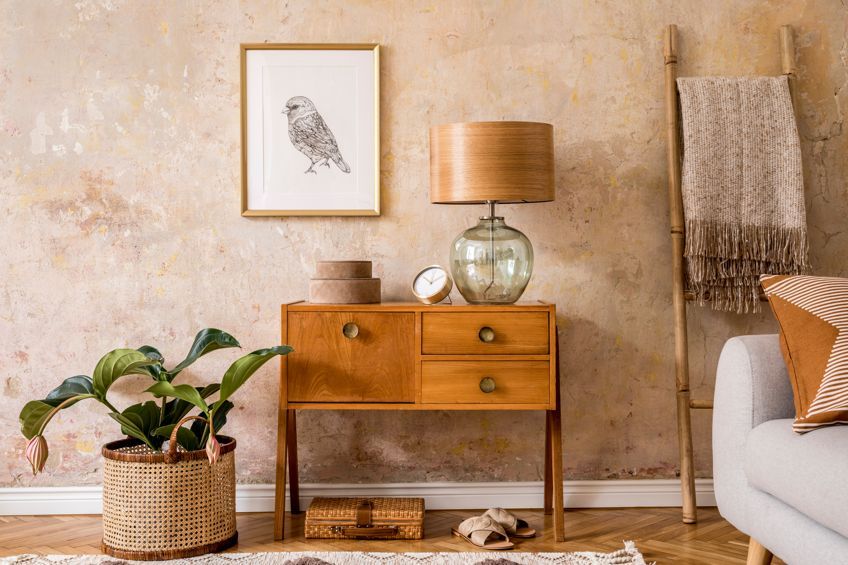

When it comes to working with three or more colors within a design, designers usually make use of the 60:30:10 rule. This division of color use helps to create a balance and prevents all the colors from becoming too overwhelming.
So, you will choose the main color, and this will become 60 percent of your design. The 30 percent will then be your first accent color, and the 10 percent will just be a pop of color here and there. For example, when implementing an interior design, you can use the main color on the walls, and in other areas like larger furniture pieces, and area rugs. The next color can also be accent rugs, chairs, bedding, or even window treatments. The last color can be added through cushions, throws, art pieces, or other accessories.
You can use analogous colors for the following.
- Interior design
- Fashion design
- Advertising
- Logos
- Packaging
- Product design
- Stationary
- Art
- Movies
Tips for Using Analogous Colors
There are a few tips you can follow to help create the best analogous color schemes. Sometimes, you can understand the basic principles, but it is always good to get some practical advice you can use for your designs.
- Be aware of your color choices. Choosing the correct analogous colors can affect the outcome you wish to achieve.
- Do not overuse the colors. Analogous colors are great, but they still need to be used properly. Do not use too much of one color, but make sure the colors are balanced.
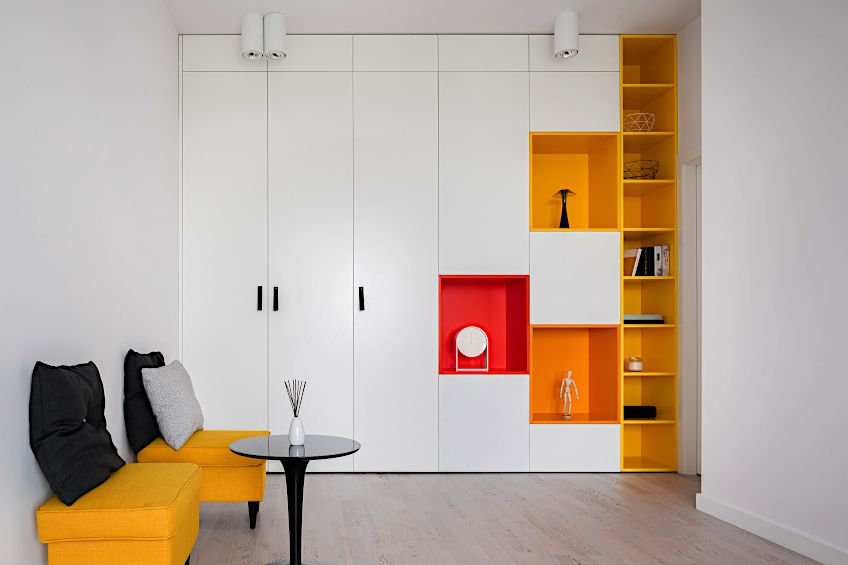

- Experiment with different hues. Play around with various tints, shades, and tones of analogous colors until you find the perfect match. Lighter colors can have a minimalistic and soft look, while darker colors are more daring.
- Incorporating contrast. You can bring in some contrast through different textures and shapes, which can help to spice up the design.
Understanding how to work with colors and how to apply analogous colors goes a long way to helping produce some amazing designs. So, the next time you are looking for a more cohesive and pleasing design, consider an analogous color scheme.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Analogous Colors?
These are a group of three colors that have similar traits and can usually be found close to one another on the color wheel. For example, green, yellow-green, and yellow. These colors work well together and are pleasing to look at, creating a harmonious effect.
Are Analogous Colors Warm or Cool?
This will depend on the main color you choose. If you decide on blue, green, or purple as your main color, then it will be cool. However, if you choose red, orange, or yellow, the combination will be warm.
What Are the Analogous Colors of Brown?
Technically, brown is not one of the colors found on the color wheel. However, brown is usually a mixture of red and yellow, so all other shades of red and yellow will help create a brown analogous color scheme.
In 2005, Charlene completed her Wellness Diplomas in Therapeutic Aromatherapy and Reflexology from the International School of Reflexology and Meridian Therapy. She worked for a company offering corporate wellness programs for a couple of years, before opening up her own therapy practice. It was in 2015 that a friend, who was a digital marketer, asked her to join her company as a content creator, and this is where she found her excitement for writing.
Since joining the content writing world, she has gained a lot of experience over the years writing on a diverse selection of topics, from beauty, health, wellness, travel, and more. Due to various circumstances, she had to close her therapy practice and is now a full-time freelance writer. Being a creative person, she could not pass up the opportunity to contribute to the Art in Context team, where is was in her element, writing about a variety of art and craft topics. Contributing articles for over three years now, her knowledge in this area has grown, and she has gotten to explore her creativity and improve her research and writing skills.
Charlene Lewis has been working for artincontext.org since the relaunch in 2020. She is an experienced writer and mainly focuses on the topics of color theory, painting and drawing.
Learn more about Charlene Lewis and the Art in Context Team.
Cite this Article
Charlene, Lewis, “Analogous Colors – What Are Analogous Colors in Color Theory.” Art in Context. January 2, 2023. URL: https://artincontext.org/analogous-colors/
Lewis, C. (2023, 2 January). Analogous Colors – What Are Analogous Colors in Color Theory. Art in Context. https://artincontext.org/analogous-colors/
Lewis, Charlene. “Analogous Colors – What Are Analogous Colors in Color Theory.” Art in Context, January 2, 2023. https://artincontext.org/analogous-colors/.









