What Is Digital Art? – A Look at the Exciting Digital Art Movement
What is Digital art, exactly how does Digital art work, and what is a Digital Artist? In this article, we will be answering these questions and more. We will be exploring the history of Digital art and discovering various Digital art types. Is Digital art real art or do Digital drawings fall short of human ability?
What Is Digital Art?
Digital art may be defined as an artistic activity or work that incorporates digital technology into the creation or production process, or as computerized art that employs and interacts with digital media. When was Digital art invented?
The Digital art movement began in the 1960s and has steadily become more powerful and prominent in our daily lives.
History of Digital Art
After some initial opposition, digital technology’s effect has revolutionized activities such as sculpture, writing, painting, drawing, and music, while new approaches such as digital installation art, net art, and virtual reality have arisen.
Andy Warhol made Digital art on a Commodore Amiga, which was officially unveiled in July 1985 at the Lincoln Center in New York. Debbie Harry’s image was recorded in monochrome using a video camera and processed using the graphics application ProPaint. Warhol added color to the image by employing flood fills.
Is Digital Art Real Art or Just a Modern Trend?
On the subject of whether Digital art qualifies as genuine art, there has been significant discussion and disagreement. If by “real”, you mean did the final product actually use actual physical equipment to create actual physical items? So, no.
However, Digital art may also be referred to as genuine art because it calls for a lot of the same faculties and methods of creativity as traditional art.
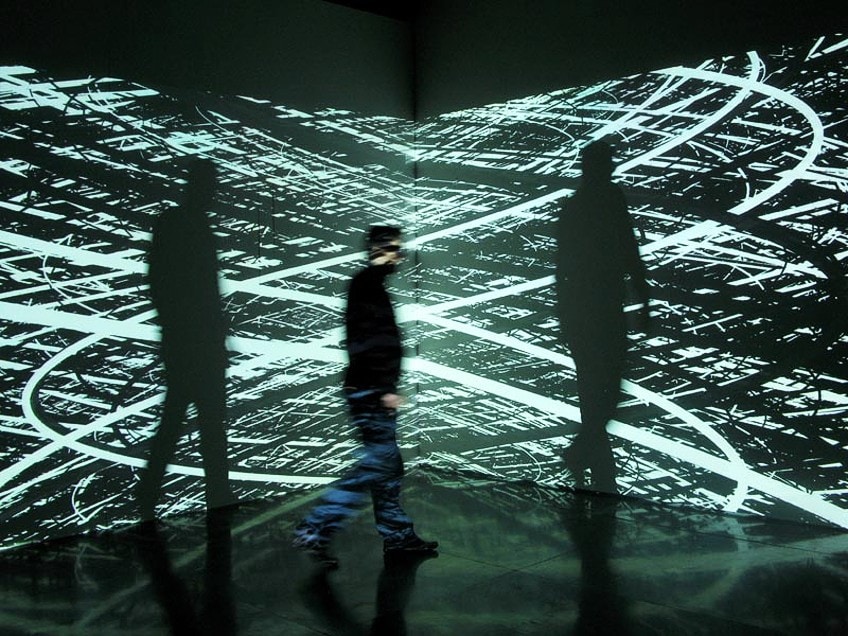

Irrespective of the medium, the main goal of all art is to communicate the feelings of the creator. Digital art creation demands the same level of ability, creativity, originality, expertise, and work that conventional art does.
Irrespective of the material, every artist needs to come to master their tools.
Have Digital Drawings Overtaken Traditional Artworks in Popularity?
Because of your online presence, you could be more familiar with Digital art, however, it’s difficult to determine whether it’s truly more well-liked. Digital art is considerably easier to share and publish than traditional art, which is maybe why it is so well-liked online.
Due to its convenience, Digital art is also favored by many novices.
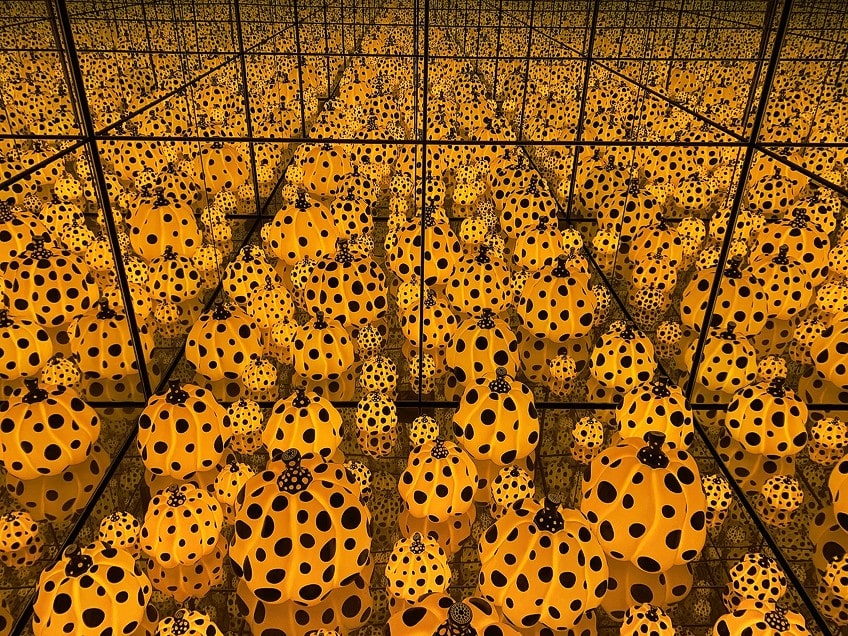

Digital and traditional art components are combined in many current, well-liked exhibitions on display all around the world. For instance, Yayoi Kusama’s work combines traditional and contemporary media and consistently draws record crowds to exhibitions.
Older conventional works by painters like Vincent van Gogh have been digitally preserved in recent “immersive” digital exhibitions, allowing more spectators to enjoy works that were formerly much more challenging to see.
The Advantages and Disadvantages of the Digital Art Movement
There are numerous benefits and drawbacks to Digital art. One advantage of digital art is that it is much more practical than conventional art since it requires less setup and requires you to gather fewer instruments, such as paintbrushes and paints.
Due to the fact that most faults can be corrected with simply a click of a button, it is also far more lenient than traditional art.
Digitally saved artwork is also considerably simpler to keep and transport than other conventional art formats. If the necessity arises, artists may easily deliver their works digitally with a few mouse clicks. This method makes Digital art more approachable, universal, and impactful.
Digital art has the disadvantage of lacking the personal connection, tactile nature, and sensation you receive from actually applying pencils or brushes to paper.
Digital Art Types
Digital art can come from various sources, such as a scanned photograph or an image created using vector graphics programs utilizing a mouse or drawing tablet, or it can be entirely computer-generated (like fractals and computational art).
Digital paintings are works of art that are generated in a similar way to traditional paintings, but with the aid of computer software, and then digitally output the finished picture as if it were painted on canvas.
Despite differing viewpoints on the benefits and drawbacks of digital technology for the arts, there appears to be broad agreement among those involved in Digital art that it has led to a “massive expansion of the creative sphere,” or that it has greatly increased the opportunities for both professional and amateur artists to express their creativity.
Computer-Generated Media
Digital visual art may either be 2D visual data projected on a digital display device or 2D visual information computationally transformed into 3D information. The most basic is 2D computer graphics, which mimic how you might sketch on paper and a pencil. But in this instance, the drawing tool may be a mouse or a pad stylus since the image is on a computer screen. What is created on your screen can seem to have been painted, written, or drawn with a pencil.
The second type is 3D computer graphics, where you arrange items to be “photographed” by the machine while the screen transforms into a doorway into a virtual environment.

In contrast to 3D computer graphics, which employ vector graphics to create realistic virtual reality installations, 2D computer graphics often use raster images as their primary method of data source presentations. The creation of 2D or 3D art only through the implementation of algorithms written into computer programs constitutes a potential third paradigm.
A discussion with computer art innovator Frieder Nake provides an overview of the history of what might be regarded as the native art form of the computer.
3D Computer-Generated Images
For usage in a variety of media, including cinema, television, publishing, quick prototyping, games, and special effects, 3D images are produced via the technique of generating visuals using geometric forms, polygons, or NURBS curves.
There are several software tools available for this.
With the use of technology, people may work together, exchanging ideas and enhancing one another’s work in a way akin to the open-source movement and the creative commons, where people can work together on projects to produce art.
Ray Caesar, a pop surrealist artist, uses Maya, a 3D modeling program for digital animation, to build both his virtual worlds and the characters that inhabit them.
Computer-Generated Animation
Animations produced by a computer using digital models made by 3D designers or programmatically generated are known as computer-generated animations. The phrase is typically used to describe works made totally by computers.
Computer-generated graphics, sometimes known as computer-generated images (CGI) in the film business, are frequently used in movies.
Although films have been employing considerable computer imagery since the mid-70s, CGI evolved enough in the 1990s and early 2000s to make it feasible to produce realistic 3D computer animation for the first time.
Many contemporary movies have drawn attention for heavily utilizing photorealistic CGI.
Art Created Specifically for Digital Media
The term “Digital art” is largely used in contemporary art to refer to visual works of art that are highly computational and overtly interact with digital technologies. It is extremely difficult to establish a generalization about the art form by classifying all works of art that utilize digital technology at some point in their creation and distribution as Digital art, according to art historian Christiane Paul.
Digital Installation Art
Digital installation art includes a wide range of mediums and activities. Some of them resemble video installations, especially large-scale pieces with projections and real-time video recording. Numerous digital installations make an effort to create immersive settings by utilizing projection techniques that improve an audience’s perception of sensory envelopment. Some go even further and make an effort to promote total immersion in virtual worlds.
This kind of installation is frequently site-specific, scalable, and non-dimensional, which allows it to be rearranged to fit various presentation venues.
Blockchain Art
Since the NFTs frenzy of 2020 and 2021, blockchain and more especially NFTs have become connected with Digital art. Although the technology has drawn criticism and has many weaknesses about plagiarism and fraud (because of its largely unregulated nature), auction houses like Sotheby’s and Christie’s and numerous galleries and museums around the world began collaborating and alliances with Digital artists.
Galleries began selling NFTs related to digital artworks and spotlighting those works of art both in simulated galleries and real-life.
The Use of Digital Archives
In addition to the production of unique works of art, artificial intelligence-based research techniques have been developed to statistically examine Digital art collections. The extensive digitalization of artwork over the past few decades has made this feasible.
Although the availability and investigation of these collections were the primary goals of digitalization, the application of AI in their analysis has opened up new study horizons.
The basic methods for analyzing Digital art use two computing techniques: close scanning and distant seeing. Close scanning focuses on particular visual facets of a single work. Analyzing brushstrokes or textural qualities, as well as computational artist authentication, are among activities carried out by machines in close reading techniques.
How Does Digital Art Work?
Digital art may be created in a variety of ways with various technology and software. To begin, though, you need some ability and diligence to make Digital art. A sketching tablet with a pen, as well as programs like Photoshop, For the program to run, you also need a PC or laptop. The final component is inexpensive: inventiveness and creativity. Due to the high learning curve of transitioning to a new medium and understanding all the subtleties of the numerous tools needed, transitioning from conventional to digital forms may be challenging for established artists or even for beginners.
However, it doesn’t necessarily require more expertise than conventional forms of art; it just takes some getting used to and skill building.
Because mistakes can be corrected without any repercussions, Digital art can often be simpler than drawing. With so many varied tools and settings at an artist’s disposal, digital media is also far more practical and simpler to use for coloring, blending, shading, etc.
Other talented artists, nevertheless, could find it challenging to grasp the new tools needed to produce Digital artworks.
Similar fundamental creative abilities are still necessary for creating Digital art, and artists must be skilled in using a variety of software programs. However, because it is much simpler to get into and doesn’t require a lot of setups, space, or creative supplies, it may be more forgiving and appealing to novices.
That concludes our look at the history of Digital art and the various Digital art types. Perhaps you would like to give digital drawing a go yourself. Nowadays, becoming a part of the Digital art movement is easier than ever! Digital art is the future of art in many aspects, and getting to grips with the technology could put you on the cutting edge of design. Perhaps traditional artforms will never fully disappear, but there is nothing to lose from embracing new technologies and advancements in art.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is a Digital Artist?
There are several job options available to Digital artists. Many of these include creating animated pictures and visual effects for various media, including movies and video games. Companies that produce movies, run commercials, make video games, and create software are hiring Digital artists. If you work as a Digital artist, you may create anything from a doodle to a sculpture using computer software. These may then develop into 3D interactive visuals for sites or visual personalities, based on your industry. You can choose to focus on a particular area, such as animating, audiovisual, or game design. Whatever field you decide to work in, creativity should be your main priority.
When Was Digital Art Invented?
When computer developers created a paint software that was utilized by the very first digital designer Harold Cohen in the early 1980s, the term Digital art was first used. This robotic device, dubbed AARON, was created to create enormous designs on paper that were laid on the ground. Since making this early venture into AI, Cohen has worked to improve the AARON algorithm as science and technology advance.
How Does Digital Art Work?
Work created with or shown using digital technology is referred to as Digital art. This covers artwork created entirely on a computer as well as hand-drawn artwork that has been scanned into a computer and polished using a program like Adobe Illustrator. Motion, 3D virtual sculptural renderings, and technological hybrid projects are some examples of Digital art. Video pictures are also sometimes altered in Digital art.
In 2005, Charlene completed her Wellness Diplomas in Therapeutic Aromatherapy and Reflexology from the International School of Reflexology and Meridian Therapy. She worked for a company offering corporate wellness programs for a couple of years, before opening up her own therapy practice. It was in 2015 that a friend, who was a digital marketer, asked her to join her company as a content creator, and this is where she found her excitement for writing.
Since joining the content writing world, she has gained a lot of experience over the years writing on a diverse selection of topics, from beauty, health, wellness, travel, and more. Due to various circumstances, she had to close her therapy practice and is now a full-time freelance writer. Being a creative person, she could not pass up the opportunity to contribute to the Art in Context team, where is was in her element, writing about a variety of art and craft topics. Contributing articles for over three years now, her knowledge in this area has grown, and she has gotten to explore her creativity and improve her research and writing skills.
Charlene Lewis has been working for artincontext.org since the relaunch in 2020. She is an experienced writer and mainly focuses on the topics of color theory, painting and drawing.
Learn more about Charlene Lewis and the Art in Context Team.
Cite this Article
Charlene, Lewis, “What Is Digital Art? – A Look at the Exciting Digital Art Movement.” Art in Context. July 20, 2022. URL: https://artincontext.org/what-is-digital-art/
Lewis, C. (2022, 20 July). What Is Digital Art? – A Look at the Exciting Digital Art Movement. Art in Context. https://artincontext.org/what-is-digital-art/
Lewis, Charlene. “What Is Digital Art? – A Look at the Exciting Digital Art Movement.” Art in Context, July 20, 2022. https://artincontext.org/what-is-digital-art/.









