Maurice de Vlaminck – A Key Member of the Fauvist Movement
Maurice de Vlaminck was a pioneering French artist who played a pivotal role in the Fauvist movement, characterized by its bold use of color and emotive brushwork. Alongside contemporaries like André Derain and Henri Matisse, Vlaminck’s vibrant landscapes and expressive compositions challenged traditional approaches to color and form, earning him a prominent place in early 20th-century modern art. His work evolved over time, transitioning from the explosive hues of Fauvism to a more subdued palette influenced by Cézanne and the burgeoning Cubist movement. Vlaminck’s legacy lies in his fearless experimentation and his profound impact on the trajectory of modern painting.
Key Takeaways
- Maurice de Vlaminck was a key figure in the Fauvist movement.
- His artwork is characterized by bold colors and expressive brushwork.
- Vlaminck’s influence on modern art remains significant.
Early Life and Influences
| Birth | April 4, 1876 |
|---|---|
| Death | October 11, 1958 |
| Place of Birth | Paris, France |
| Genre of Work | Fauvism and Expressionism |
Maurice de Vlaminck, a prominent French painter born on April 4, 1876, played a key role in the formation of the Fauvist movement. Alongside André Derain and Henri Matisse, he was one of the leading figures who revolutionized modern art with their use of intense and expressive colors. This group, known for their wild brushwork and vivid palette, challenged traditional artistic conventions and laid the groundwork for future avant-garde movements.
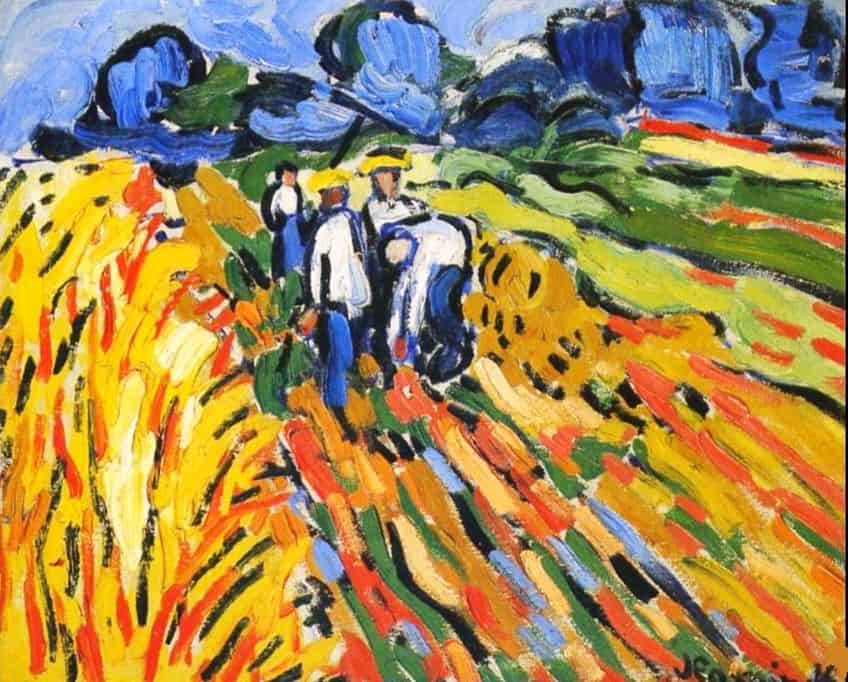

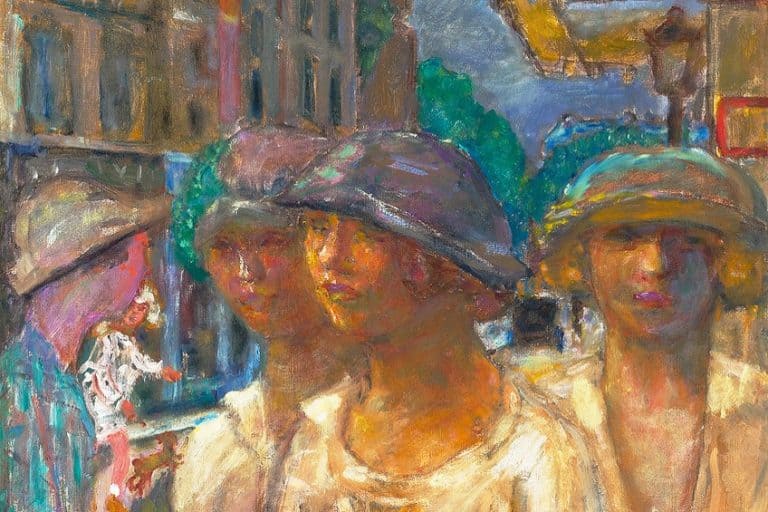
Vlaminck’s works are notable for their bold use of primary colors and dynamic, short brushstrokes. His paintings often feature vibrant landscapes, city scenes, and portraits that capture the energy and emotion of the early 20th century. His distinct style not only pushed the boundaries of color theory but also influenced a generation of artists who followed in his footsteps. Exploring the life and legacy of Maurice de Vlaminck offers a fascinating glimpse into the transformative period of Fauvism and shows how his innovations left a lasting impact on modern art.
His contributions continue to be celebrated for their daring and originality.
Artistic Influences
Vlaminck was heavily influenced by Vincent van Gogh, whose bold color choices and expressive brushwork resonated with him. The works of Henri Matisse and Paul Cézanne also left a lasting impression on his artistic journey. Vlaminck admired Toulouse-Lautrec for his dynamic compositions and vivid palette. These influences pushed Vlaminck to embrace a vivid and bold style, characteristic of the Fauve movement, known for its explosive use of color.

Personal Background
Maurice grew up in Paris but moved to Le Vésinet with his family when he was three. His father taught violin, and his mother taught piano, which surrounded him with a rich musical environment. Despite his strong family ties to music, Vlaminck was naturally drawn to visual arts. He briefly pursued various other interests, including cycling and acting, before fully dedicating himself to painting.
This background of diverse experiences contributed to his multifaceted approach to art.
Mature Period
During his mature period, Vlaminck developed his unique style that stood out in the early 20th-century art scene. He integrated intense colors and vigorous brushstrokes into his paintings, diverging from the more subdued tones of the Impressionists. Vlaminck’s rejection of academic art traditions helped him carve out a distinct niche. His works often featured landscapes and urban scenes, capturing the energy and movement of modern life with a vivid palette.

Later Period and Death
In Vlaminck’s later years, his style evolved. He moved away from the extreme vibrancy of Fauvism towards more muted tones and subtler expressions. His later work showed a deep appreciation for Cézanne’s structured compositions and a refined use of color. Vlaminck continued to paint until his death on October 11, 1958, in Rueil-la-Gadelière, France.
Even in his final years, Vlaminck remained dedicated to his art, leaving behind a legacy defined by his innovative use of color and form.
Fauvism and Relationship With Contemporary Artists
Maurice de Vlaminck played a significant role in the Fauvism movement. His interactions with contemporaries like André Derain and Henri Matisse shaped his work and the overall direction of Fauvism.

Collaboration With André Derain
Vlaminck started collaborating with André Derain around 1900 in Chatou, near Paris. Both artists shared a passion for vivid colors and bold brushwork. This friendship and collaboration were crucial in the development of Fauvism. Derain’s influence can be seen in Vlaminck’s work where they often painted similar scenes, yet each brought a unique perspective.
By working together, they pushed each other to experiment more boldly with color and form.
Salon d’Automne and Fauve Movement
The Salon d’Automne exhibition of 1905 was a pivotal moment for Fauvism. It was during this show that the term “Fauves,” meaning “Wild Beasts,” was coined by art critic Louis Vauxcelles to describe the vivid, emotive works of Vlaminck, Matisse, Derain, and others. Vlaminck’s use of intense color and disregard for realistic representation shocked viewers. His contributions to the exhibition helped solidify the Fauve movement as a significant avant-garde style. The vibrant and dynamic works presented there marked a break from traditional methods and highlighted a new artistic direction.

Rivalry and Friendship With Henri Matisse
Vlaminck had a complex relationship with Henri Matisse. While they both were leaders of the Fauve movement, their styles and temperaments often put them at odds. Matisse was more controlled and methodical in his approach, whereas Vlaminck was spontaneous and impulsive. These differences led to both rivalry and mutual respect. Matisse’s influence can be seen in Vlaminck’s pursuit of color, but Vlaminck kept his unique, raw energy.
Their interactions enriched the movement, sparking new ideas and innovation.
Artistic Style and Notable Works
Maurice de Vlaminck was a French painter known for his vibrant use of color and his involvement in the Fauve movement. He created several notable paintings that stand out for their intense hues and bold brushwork.

Painting Technique
Vlaminck’s technique was characterized by bold, expressive brushstrokes and the use of vivid, non-naturalistic colors. He often applied paint directly from the tube onto the canvas, creating a textured surface. This approach gave his works a raw and powerful energy. He preferred using bright reds, deep blues, and rich greens, with little concern for realistic color representation.
The painting Houses at Chatou is a prime example, where he used intense colors to depict simple houses and landscapes with a dynamic flair.
Evolution of Style
In the early 1900s, Vlaminck was a key figure in Fauvism, a movement that emphasized strong color over realistic values. His early works from this period, like La Seine à Chatou, are marked by their vibrant color contrasts and remarkable simplicity. Later in his career, his style evolved to incorporate more muted tones and a focus on structured compositions. Though these later works lacked the bold color schemes of his Fauvist period, they still maintained a distinct expressiveness and depth. Both phases of his career contributed significantly to his reputation as a pioneering modern painter.

Significant Artworks by Maurice de Vlaminck
Maurice de Vlaminck created numerous influential paintings, many of which shaped the modern art world. He was a prominent figure in the Fauvist movement, renowned for his daring use of color. One prominent painting is Le Diable au Corps (The Devil in the Flesh), completed in 1926. This work showcases Vlaminck’s intense and emotion-driven style, emphasizing raw and vivid colors. Tournant Dangereux (Dangerous Corner), painted in 1930, is another significant piece. This artwork captures dramatic scenes with striking contrasts, highlighting Vlaminck’s masterful use of light and shadow. In 1921, he created Trois Journées de la Tribu (Three Days of the Tribe). This painting is notable for its vibrant colors and dynamic composition, reflecting the artist’s unique approach to capturing movement and life. Another important work is Voyages, done in 1920. This painting exudes a sense of adventure and exploration, with bold strokes and a vivid palette. These artworks display Vlaminck’s distinctive style and his contribution to the Fauve movement.
Each piece reveals his skill in manipulating color and emotion, making his work stand out in the art world.
Legacy and Impact on Modern Art
Maurice de Vlaminck left a significant mark on modern art with his vibrant use of color and intense emotional expression. He inspired many artists and was recognized worldwide for his contributions to the art world.
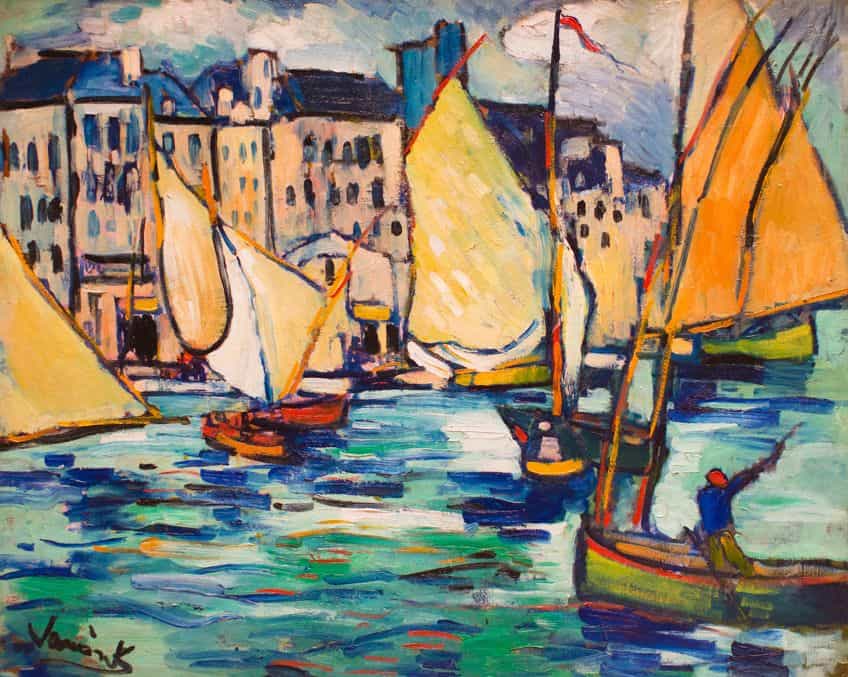
Contributions to Modern Art
Maurice de Vlaminck was a key figure in the Fauve movement alongside Henri Matisse and André Derain. Known for his bold use of primary colors and emotive brushstrokes, he broke away from traditional forms and techniques. This movement, lasting from 1904 to 1908, emphasized intense color over representational accuracy. Vlaminck’s works often depicted landscapes and cityscapes with vivid hues and dynamic compositions. He also experimented briefly with Cubism, though he eventually returned to his Fauvist style. His paintings are noted for their uninhibited, raw energy and vivid palette, which conveyed deep emotional resonance.
These characteristics distinguished his work, making significant contributions to modern art’s evolution.
Influence on Later Artists
Vlaminck’s approach to color and emotion influenced many artists beyond his time. His work encouraged others to explore bold color palettes and expressive techniques. Artists such as the German Expressionists drew inspiration from his daring use of color and form. Even contemporary modern artists owe a debt to Vlaminck for paving the way for more expressive and abstract styles. His emphasis on emotion and subjective experience over realistic depiction left a lasting imprint on the art world, allowing future generations to push boundaries and develop new art forms.

Recognition and Representation
During his lifetime, Maurice de Vlaminck received recognition from art critics and galleries. His works were exhibited in influential venues such as the Salon d’Automne, where his vibrant canvases challenged and captivated audiences. Today, major museums around the world, including the Museum of Modern Art (MoMA), house his paintings in their collections. Exhibitions continue to showcase his work, reaffirming his place in art history. The Artists Rights Society protects his works, ensuring his legacy endures.
Prominent art historians and critics frequently cite him as a pioneering figure in modern art, underscoring his lasting influence.
Legacy of Maurice de Vlaminck Today
Maurice de Vlaminck’s legacy persists in contemporary culture. Art schools and universities study his techniques and contributions, providing valuable lessons for emerging artists. His works are still published in art books and featured in exhibitions, ensuring that new audiences discover his impact. Collectors highly value his paintings, and his work fetches significant prices at auctions. The continued interest and admiration for Vlaminck’s art highlight its timeless appeal. His legacy lives on in the vibrant, emotive, and bold expressions found in modern art today.

Maurice de Vlaminck’s artistic journey encapsulates the fervent spirit of early 20th-century modernism. From his revolutionary contributions to Fauvism, with its daring color palettes and emotive intensity, to his later explorations of structure and form influenced by Cézanne and Cubism, Vlaminck remained a dynamic and influential figure in the art world. His ability to continually evolve while staying true to his expressive vision highlights his versatility and commitment to artistic innovation. Vlaminck’s legacy endures, reflecting the transformative power of color and the boundless possibilities of modern art.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are the Defining Features of Maurice de Vlaminck’s Fauvist Artworks?
Maurice de Vlaminck’s Fauvist artworks are characterized by their bright, bold colors. He often used thick, expressive brushstrokes. His paintings typically depict landscapes and suburban scenes. Vlaminck’s work from this period reflects his desire to break away from traditional artistic norms and embrace a more emotional and spontaneous style.
What Are Some Interesting Facts About Maurice de Vlaminck’s Life and Career?
Maurice de Vlaminck was born on April 4, 1876, in Paris. He was a self-taught artist who shunned formal academic training. Alongside André Derain and Henri Matisse, Vlaminck was a leading figure in the Fauve movement. He was also a talented writer and musician. Despite his lack of formal training, Vlaminck became one of the most influential artists of his time.
How Would You Describe Maurice de Vlaminck’s Influence on the Art World?
Maurice de Vlaminck played a crucial role in the development of modern art. His bold use of color and expressive techniques influenced many artists. His works at the Salon d’Automne exhibition in 1905 were among the most controversial and groundbreaking of the time. Vlaminck’s commitment to artistic freedom and expression helped shape the future of contemporary art.
Can You Identify Maurice de Vlaminck’s Unique Signature on His Artworks?
Maurice de Vlaminck’s signature is often straightforward and legible. He typically signed his works Vlaminck in a clear, simple script. This signature can usually be found on the bottom corner of his paintings. His signature is an important aspect for art collectors and historians in authenticating his pieces.
Isabella studied at the University of Cape Town in South Africa and graduated with a Bachelor of Arts majoring in English Literature & Language and Psychology. Throughout her undergraduate years, she took Art History as an additional subject and absolutely loved it. Building on from her art history knowledge that began in high school, art has always been a particular area of fascination for her. From learning about artworks previously unknown to her, or sharpening her existing understanding of specific works, the ability to continue learning within this interesting sphere excites her greatly.
Her focal points of interest in art history encompass profiling specific artists and art movements, as it is these areas where she is able to really dig deep into the rich narrative of the art world. Additionally, she particularly enjoys exploring the different artistic styles of the 20th century, as well as the important impact that female artists have had on the development of art history.
Learn more about Isabella Meyer and the Art in Context Team.
Cite this Article
Isabella, Meyer, “Maurice de Vlaminck – A Key Member of the Fauvist Movement.” Art in Context. July 10, 2024. URL: https://artincontext.org/maurice-de-vlaminck/
Meyer, I. (2024, 10 July). Maurice de Vlaminck – A Key Member of the Fauvist Movement. Art in Context. https://artincontext.org/maurice-de-vlaminck/
Meyer, Isabella. “Maurice de Vlaminck – A Key Member of the Fauvist Movement.” Art in Context, July 10, 2024. https://artincontext.org/maurice-de-vlaminck/.











