Genre Painting – The Depiction of Everyday Life in Art
What is a genre painting, and what are some famous examples of genre artwork? The art of genre painting was derived from the 16th-century art practice of painting subjects that were the most typical and distinguished from that of similar subjects depicted in traditional paintings. These began as historical compositions and scenes of peasants to scenes of everyday life and evolved into the 17th century as an established genre art. In this article, we will explore the definition of genre painting, as well as its development and evolution in art history, and a few famous art pieces that will help you grasp this style of painting. Read on for more about this unique painting style!
A Genre Painting Definition: Introduction to Genre Art
What is a genre painting, and how did this art practice emerge? Genre painting is commonly known as the petit genre, which aims to depict scenes from everyday life that are common. This type of genre art includes paintings that showcase common activities and engagements between people and generally display figures that have no fixed identity. Genre painting differs from history painting, which is known for its own style, and grand genre, and depicts specific scenes from a narrative.
While some genre works showcase figures that could arguably be identified as models that the artist knew of, scholars may struggle to differentiate whether the artist intended for the work to be a portrait instead of a genre painting.
What is incredible about genre painting is that the style and approach to the subject can be romantic, imagined, or realistic, which truly highlights how much freedom artists had to experiment with different themes. Genre paintings were also incredibly popular among the middle class and bourgeoisie and also appear in tombs, as far back as thousands of years ago.

Other types of art that showcase elements of genre painting include Medieval illuminated manuscripts that often include scenes of peasant life and are widely recognized in texts such as the Très Riches Heures du Duc de Berry (c. 15th century) with images of the Labours of the Months, which showcases many rural scenes and activities that took place during specific months.
From agrarian scenes to banquets, barber shops, and pubs, genre painting offers insight into the cultures of the past and the livelihoods of common people.
It is also important to distinguish the term “genre painting” from the widely understood term “genre”, which refers to a type of art or painting. Genre paintings are broad yet specific in their regional and historical contexts.
The Development of Genre Painting
Genre painting began as early as the age of antiquities but was formally recognized as a genre art form in the 17th century with painters from the Flemish Baroque and Dutch Golden Age schools producing works that were recognized as such. Areas such as the Low Countries in Europe were best known for their contribution to genre painting until the 18th century.
Early genre paintings included themes and subjects relating to religion and morals and were best captured in the large-scale genre paintings of Jan Sanders van Hemessen during the early 16th century.
Paintings produced in Antwerp also famously provided works that became known as “Mannerist inversion” paintings, which emphasized elements that were previously hidden in the background by focusing on them as subjects. Other well-known 16th-century genre painters included Joachim Beuckelaer and Pieter Aertsen, who included scenes of market traders, cooks, and bountiful harvests while leaving religious scenes as minor elements in the background.

Dutch and Flemish Renaissance masters such as Pieter Bruegel the Elder also embraced this inversion and focused his attention on common subjects. Many painters of the Low Countries had their works purchased by middle-class families, who would buy their works for display in their homes and decoration.
Symbolic and moral meanings were also attached to 17th-century genre paintings, which initially gave the impression that this type of art was intended to showcase realistic styles of painting everyday subjects.
However, Flemish and Dutch genre paintings had much more depth to their use of realistic painting techniques than perceived. Artists such as Jan Steen and Jacob Jordaens also used genre painting to highlight certain morals that society ought to acknowledge.
Common Themes in Genre Painting
Popular themes and subjects in genre painting included merry celebrations and joyous company, which was often illustrated as a group of people enjoying themselves among one another in a festive environment. The Roman countryside was another niche theme for genre painters, particularly among the collective of artists known as the Bentvueghels. In France, artists such as Louis le Nain were highly influential in the development of genre painting in the 17th century and explored depictions of common folk in gathering settings at home.
In the 18th century, genre painting saw a complete spike in the interest in everyday scenes in painting and a shift toward realism with portraits and detailed scenes inspiring many 19th-century artists.
English painters such as William Hogarth also propelled genre painting as a tool for social critique, humor, and moral lessons that were illustrated through people jam-packed with narrative details. Flemish painters working from Spain also influenced the spread of genre painting, which led to the development of picaresque genre scenes in the 17th century during the Spanish Golden Age.

Bodegone scenes in Spain also emerged as a theme in genre painting during this era and were popular among artists such as Diego Velázquez and Bartolomé Murillo. Themes of the human condition and suffering were further explored by painters such as Francisco de Goya, with his most notable genre works produced between 1810 and 1823.
Stylistic Shifts in the 19th Century
The 19th century saw a radical decline in the popularity of history and religious painting in art since many artists began to adopt the themes and appeal of genre painting through scenes from everyday life. Famous Realists such as Gustave Courbet revolutionized genre painting by elevating the scale of his paintings that were previously used for historical works that were considered “more important”. The Troubadour style reflected how history painting had shifted with the introduction of Realism and the acceptance of genre scene subjects as part of history.
Throughout the 19th century, genre painting remained alive and well through the works of artists such as Jean-Louis-Ernest Meissonier, Sir David Wilkie, and William Powell Frith.

By the 20th century, new art styles born from Impressionism saw the term “genre painting” evolve its definition to encompass art that contained an anecdotal atmosphere and was created with a realistic technique. Regions such as Belgium also saw massive shifts in the adoption of 17th-century genre painting styles after 1830 to glorify the nation’s history.
Towards the late 19th century, Belgian painters such as Henri de Braekeleer defied existing genre painting conventions to create modern genre paintings that experimented with color and light.
Artists in the United States who were formally recognized as true painters of genre art included figures like John Lewis Krimmel, a German immigrant, who was strongly influenced by Scottish and English genre painters. Scenes of impoverished African American people and communities of the South following the American Civil War were also piloted by genre painters such as Harry Roseland with more modern themes born from artists such as Norman Rockwell and Ernie Barnes.
The Influence of the Protestant Reformation
Through social changes in the Roman Catholic Church, genre painting had also undergone rapid transformation in terms of its success as a form of art. In regions with a dominant Protestant population, genre painting saw an increased influence among wealthy merchants.
People who were of such status helped establish the trending themes in painting and did so as a response to the ideologies of the Roman Catholic Church.

Protestants in urban regions created a new set of values that was recognizable and offered scenes from everyday life that presented as “desirable”. The new approach was led by an unpretentious depiction of subjects that excluded sublime themes and allowed for the evolution of an individualistic culture that appreciated the mundane as an art form.
Exploring the Top Five Famous Genre Paintings
With time also comes a change in society and what it values in terms of community, culture, and environmental factors. In understanding the above development of genre painting, you can also begin to grasp the modern genre painting definition. Below, we will examine a few famous genre paintings that will provide you with excellent points of reference when studying the visual variations in genre painting and their different themes and contexts.
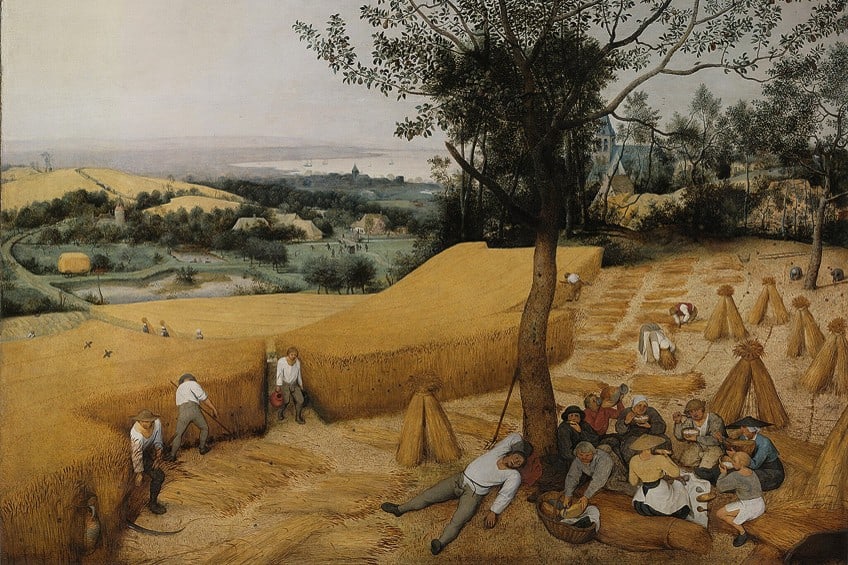
The Harvesters (1565) by Pieter Bruegel the Elder
| Artist Name | Pieter Bruegel the Elder (1525 – 1569) |
| Date | 1565 |
| Medium | Oil on wood |
| Dimensions (cm) | 119 x 162 |
| Where It Is Housed | The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York City, United States |
Also known as Pieter Bruegel I, famous genre painter Pieter Bruegel the Elder was one of the best genre painters of the 16th century. As a resident of Antwerp and a key member of a family of significant Netherlandish painters, Bruegel the Elder was considered to be an innovative artist, draftsman, and printmaker in his own right. While demonstrating a skillful eye for detail, Bruegel showcased his observations of laborers toiling in the summer heat in The Harvesters.
The painting was part of a cycle of six genre artworks representing the different periods of the year with “The Harvesters” representing the months between July and August.

His portrayal of the landscape was unidealized and presented a monumental shift in Western art with the exclusion of a religious pretext to landscape scenes. The painting was originally commissioned by a merchant named Niclaes Jongelinck, who wished to display the work in his suburban residence. Another famous genre painting by Pieter Bruegel the Elder is The Peasant Wedding (1567), which is housed at the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna.
Merry Company (1623) by Gerard van Honthorst
| Artist Name | Gerard van Honthorst (1592 – 1656) |
| Date | 1623 |
| Medium | Oil on canvas |
| Dimensions (cm) | 125 x 157 |
| Where It Is Housed | Schleißheim State Gallery, Munich, Germany |
Merry Company was created by Gerard van Honthorst in 1623 and portrays the festivities of a candle-lit scene featuring two prostitutes and a procuress, who appears to cradle an infant. The scene portrayed was meant to be provocative and alluded to the religious narrative of the prodigal son, represented by the wanton student in the presence of the women.
The illuminated pages on the table are visible by the candlelight, which also illuminates the prostitute’s semi-nude body. On one of the visible pages, there is also an illustration of a nude child, believed to represent Cupid and an old man.
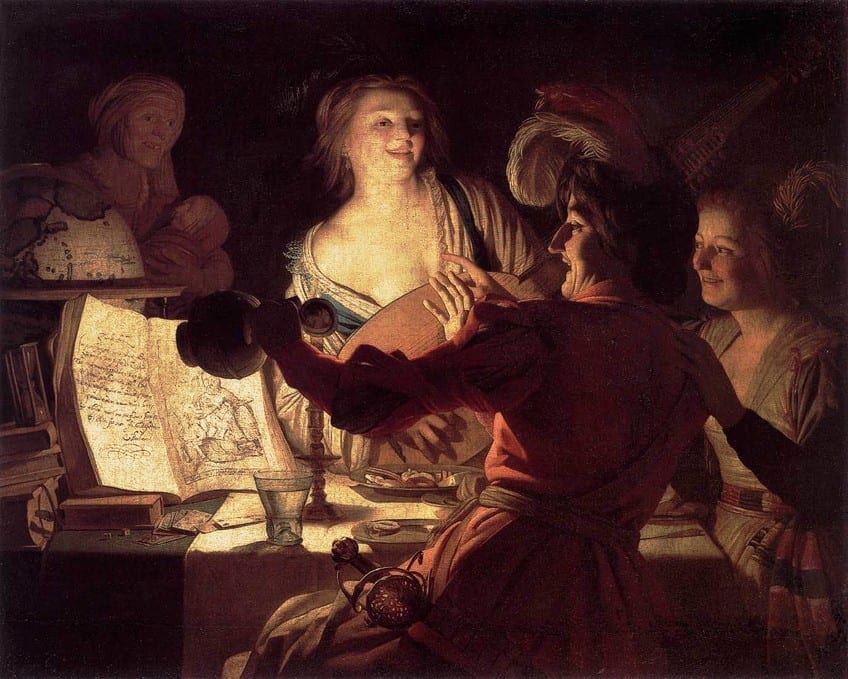

The page on the opposite side contains a Latin poem. The theme of pleasant company with subtle indications of religion and mythology is embedded in Honthorst’s painting, which he skillfully executed using the Utrecht Caravaggism style. Greatly influenced by Caravaggio, Gerard van Honthorst was most famous for his skillful depiction of artificially lit environments, for which he was also nicknamed Gherardo delle Notti.
The Poultry Seller (1662) by Gabriël Metsu
| Artist Name | Gabriël Metsu (1629 – 1667) |
| Date | 1662 |
| Medium | Oil on oak panel |
| Dimensions (cm) | 62 x 46 |
| Where It Is Housed | Gemäldegalerie, Dresden, Germany |
The Poultry Seller is perhaps one of the most famous genre paintings of the 17th century that reflects Gabriël Metsu’s intentional use of layered meaning through symbolism embedded in the suggestive depiction of the rooster’s head. The Dutch term for “birds” was also equivalent to a vulgar word for sex, which, when included in a genre scene, was quite provocative.
The painting showcases an elderly poultry trader handing over a live rooster to a younger woman. The rooster is depicted with its head craning toward the woman.

Such market scenes were popular in Flemish painting with Metsu’s painting showcasing his use of contrast to showcase a selection of other market items scattered along the bottom of the composition. Metsu’s attention to each texture and element is also remarkable as he shows off the texture and colors of wood, tree bark, a bamboo rod, basket textures, a barrel, the soft fur of a rabbit, and the skeletal textures of a bird’s head. Through his rich use of color, contrast, and narrow brush strokes, Metsu commands a more expansive style in genre painting than his contemporaries at the time.
Lady Writing a Letter With Her Maid (c. 1670 – 1671) by Johannes Vermeer
| Artist Name | Johannes Vermeer (1632 – 1675) |
| Date | c. 1670 – 1671 |
| Medium | Oil on canvas |
| Dimensions (cm) | 71.1 x 60.5 |
| Where It Is Housed | National Gallery of Ireland, Dublin, Ireland |
Lady Writing a Letter With Her Maid is among the most renowned works by Dutch master Johannes Vermeer, who created this famous genre painting between 1670 and 1671. The medium-sized oil painting represents a middle-class woman who is attended by her maid, who also appears to serve as the messenger between the woman and her lover. The painting is believed to have been inspired by Vermeer’s admiration of Ter Borch’s work and was one of Vermeer’s first experiments with using a centrifugal composition.
Vermeer depicted the maid in the mid-ground stationed behind the woman, patiently waiting for the letter to be finished. Through body language, Vermeer also highlights the fact that these two women are disconnected, which emphasizes their relationship with each other in a professional capacity.
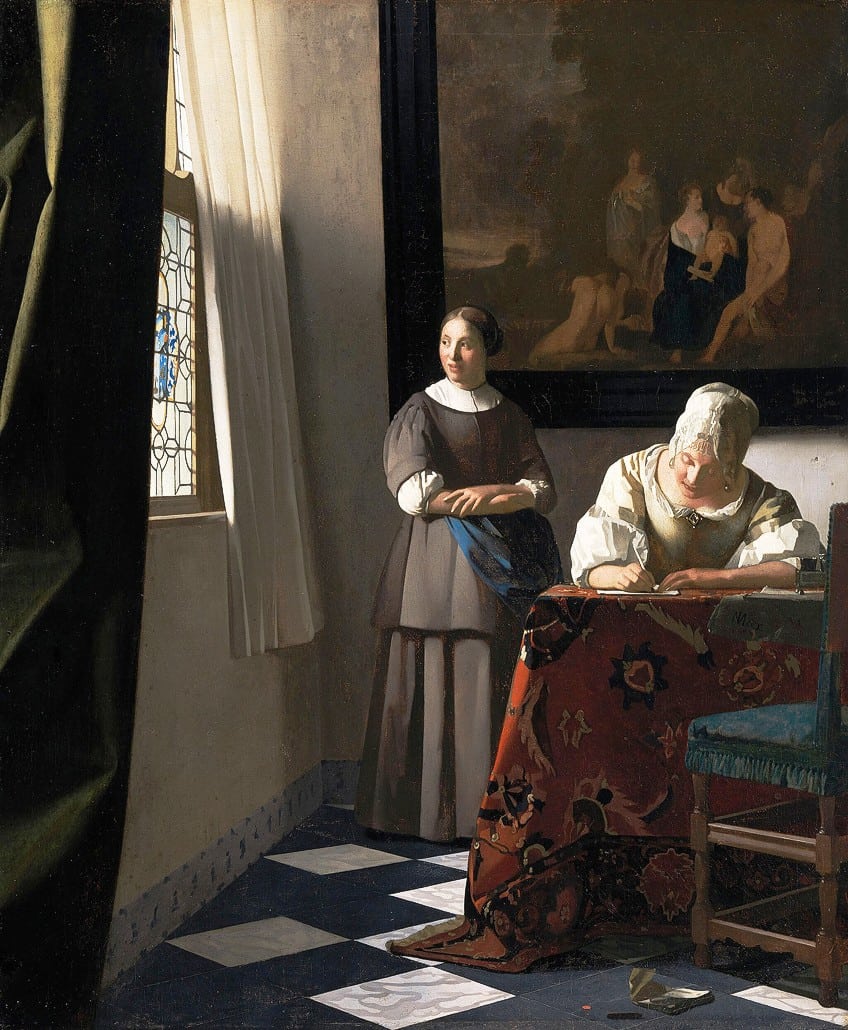

The housemaid also displays a sense of restlessness as she gazes outward, as though she is bored of waiting. While this narrative is disputed by a few scholars, others claim that the presence of the love letter itself is a connection and indication of the intimacy between the figures, despite the lack of direct emotion on the women’s faces. The famous genre painting was stolen in 1974 and later recovered during a sting operation in 1993.
Fatata te Miti (1892) by Paul Gauguin
| Artist Name | Paul Gauguin (1848 – 1903) |
| Date | 1892 |
| Medium | Oil on canvas |
| Dimensions (cm) | 68 x 92 |
| Where It Is Housed | National Gallery of Art, Washington D.C., United States |
Fatata te Miti is among the top five most famous genre paintings by post-Impressionist Paul Gauguin, which was created in 1892 on the artist’s first stay in Tahiti. Gauguin first set up his studio in Mataiea, Papeari, where he exotically captured the scene, none of which his other paintings of Tahiti represented the culture or women as he saw it.
The genre scene features two women jumping forward into the sea and are portrayed naked. In the background, there is a fisherman with a spear.
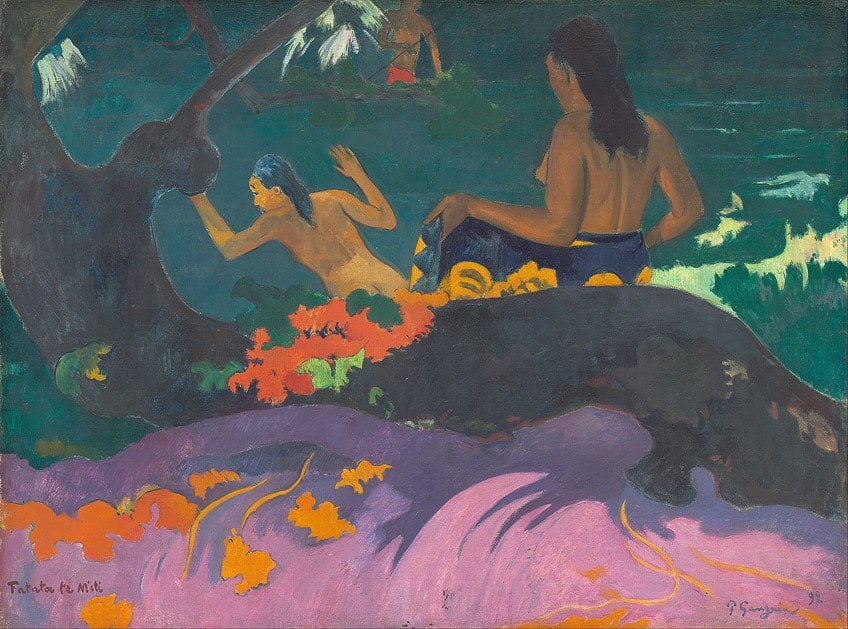

The painting represents the romanticized version of Tahiti and its people in the eyes of Gauguin, who saw the common practices of women in Tahiti as a dream come true since the Golden Age was famous for “nymphs frolicking in the waves”. This led Gauguin to embrace the subject and leverage tropical pigments to convey the sensual pleasure of his experience.
Genre Paintings in the Contemporary Era
The practice of genre painting remains a developing form of genre art that evolves with time as the existing cultural, social, economic, and political contexts shift. Today, genre painting can encompass themes of varied social experiences shared by a collective or individual. The visual language and themes of everyday life in the 21st century have certainly changed due to the many technological developments that alter the way we live life and see the world. Urban landscapes and bustling streets are examples of subjects that can be seen in genre artwork today.
Domestic genre scenes through portraiture and the illumination of the “new” mundane world we face today can be seen in the works of Modern painters such as David Hockney and the still-life compositions of Wayne Thiebaud.
While genre painting in the Contemporary period is yet to be defined, one can learn plenty from its closest art form, photography, which can be used to capture such genre scenes and blur the lines between art and documentation. Photographers such as Julie Blackmon and Juergen Teller are great examples to explore, who demonstrate elements of genre art in their practices and elevate the ordinary into works that remind us of the original 16th-century-genre paintings.

While these top five genre paintings represent a fraction of around four centuries’ worth of genre painting styles, it does give us a glimpse into the evolution of the art styles used in genre painting and the different approaches that each artist used to depict their observations. Throughout the 20th century, genre painting remained consistent and thrived among the works of Realism artists, which were notably identified in the works of the Ashcan School artists. Genre paintings in Socialist Realism can also be analyzed to observe the uses of genre painting themes in promoting propaganda.
Modern genre paintings can also be appreciated in the development of influential art styles such as Pop art, as well as the treatment of genre art with the many advancements in photographic technology.
With these many interesting points of interest that you can engage with further, we also recommend exploring the works of other prominent genre painters, including The Proposition (1631) and The Young Flute Player (1635) by Judith Leyster, The Young Beggar (1645 – 1650) by Bartolomé Esteban Murillo, The Dancing Couple (1663) by Jan Steen, and The Art of Painting (1668) by Johannes Vermeer.
We hope that these top five genre artworks have given you a glimpse into how genre scenes can be represented in painting. Through common scenes and ordinary subjects, artists like Pieter Bruegel the Elder and Gabriël Metsu have illuminated the true important subjects in art that deserve to be seen.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is a Genre Painting in Art?
Since the 16th century, paintings that portrayed the ordinary aspects of everyday life were considered to be genre paintings. These types of genre artworks initially included scenes with peasants, common marketplaces, and intimate home settings that became popular among middle-class collectors. Genre painting originated in Holland and is characterized by romantic, imagined, and realistic representations of common subjects. Over time, the genre painting definition evolved to encompass art rendered in a realistic style that demonstrates subjects with a nostalgic tone.
Who Was the Most Famous Victorian Genre Painter?
William Frith was regarded as one of the most influential and famous genre painters in Victorian England, who also specialized in large-scale paintings that depicted archetypal figures of the time.
What Popular Themes Were Depicted in Genre Paintings?
The earliest genre paintings portrayed themes such as intimate tavern gatherings, the life of peasants, celebrations, crowded markets, recreational events, interior domestic scenes, and other realistic scenes from daily life.
Jordan Anthony is a film photographer, curator, and arts writer based in Cape Town, South Africa. Anthony schooled in Durban and graduated from the University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, with a Bachelor of Art in Fine Arts. During her studies, she explored additional electives in archaeology and psychology, while focusing on themes such as healing, identity, dreams, and intuitive creation in her Contemporary art practice. She has since worked and collaborated with various professionals in the local art industry, including the KZNSA Gallery in Durban (with Strauss & Co.), Turbine Art Fair (via overheard in the gallery), and the Wits Art Museum.
Anthony’s interests include subjects and themes related to philosophy, memory, and esotericism. Her personal photography archive traces her exploration of film through abstract manipulations of color, portraiture, candid photography, and urban landscapes. Her favorite art movements include Surrealism and Fluxus, as well as art produced by ancient civilizations. Anthony’s earliest encounters with art began in childhood with a book on Salvador Dalí and imagery from old recipe books, medical books, and religious literature. She also enjoys the allure of found objects, brown noise, and constellations.
Learn more about Jordan Anthony and the Art in Context Team.
Cite this Article
Jordan, Anthony, “Genre Painting – The Depiction of Everyday Life in Art.” Art in Context. October 3, 2023. URL: https://artincontext.org/genre-painting/
Anthony, J. (2023, 3 October). Genre Painting – The Depiction of Everyday Life in Art. Art in Context. https://artincontext.org/genre-painting/
Anthony, Jordan. “Genre Painting – The Depiction of Everyday Life in Art.” Art in Context, October 3, 2023. https://artincontext.org/genre-painting/.