Max Liebermann – Discover the Founding German Impressionist
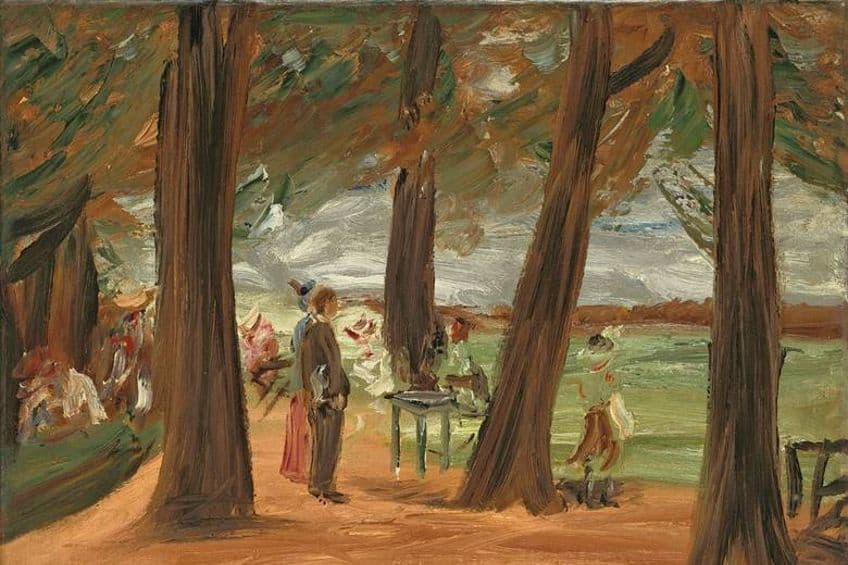
Max Liebermann was a prominent German painter and printmaker, celebrated for his significant contributions to the Impressionist and Realist movements. Born in 1847, Liebermann’s artistic journey spanned a pivotal period in European art, marked by a shift towards more modern and innovative approaches. His works often depicted everyday life scenes with a keen eye for detail and a mastery of light and color, showcasing his deep understanding of human emotion and the natural world. Liebermann’s legacy as a pioneering figure in German art continues to inspire and influence artists to this day, making him a revered and timeless icon in the art world.
Key Takeaways
- Max Liebermann is recognized for introducing and championing Impressionism in German art.
- He contributed significantly to the arts as both a painter and an influential collector.
- Liebermann’s legacy is marked by his founding of the Berlin Secession and the enduring vibrancy of his works.
Early Life and Education
| Birth | July 20, 1847 |
| Death | February 8, 1935 |
| Place of Birth | Berlin, Kingdom of Prussia (now Germany) |
| Notable Artworks |
|
Max Liebermann was a pivotal figure in the German art scene, particularly renowned for his role in bringing Impressionism to the forefront of German arts. Born in Berlin in 1847, he went on to challenge the norms of the time with his innovative painting technique and subject matter. His works often featured scenes from everyday life, capturing the beauty and dynamics of the common man’s experiences. Liebermann’s contributions were not limited to his own creations; he was also a collector, preserving and promoting French Impressionist art.

Max Liebermann’s formative years were characterized by a tension between conventional academic pursuits and his burgeoning artistic talent. He was born into a prosperous Jewish family in Berlin, and was initially steered towards a career in the fields of law and philosophy. Liebermann’s journey in art took him through rigorous training and education, including studying under the painter Carl Steffeck and honing his craft at the Weimar Art School.
As a Jewish artist in Germany, his personal life and career were affected by the sociopolitical climate of his era. Despite facing challenges, he remained a leading figure in the German art community, ultimately founding the Berlin Secession, an association that represented a progressive force in the world of German art.
Through his leadership and advocacy, he left a lasting impact on both his contemporaries and succeeding generations of artists.
Academic Pursuits and Artistic Beginnings
Liebermann was expected to join the family business, so his education began accordingly. He initially studied at the University of Berlin, where he pursued courses in law and philosophy, adhering to his family’s wishes. Despite the expectations for him to engage in a more traditional profession, Liebermann’s passion for art persisted. In his early professional life, he studied art in Weimar. During the period from 1866 to 1868, Liebermann trained under Carl Steffeck, a well-known Berlin painter. He would eventually move beyond the boundaries of his native Germany to further his art education. Notably, Liebermann spent time in the Netherlands, where he was deeply influenced by the Dutch masters.

Mature Period
Liebermann reached the height of his artistic career during what is known as the Mature Period. His studies in Paris and the Netherlands, as well as his time at the Weimar Art School from 1868 to 1872, were critical to his development.
These experiences helped Liebermann hone a style that blended naturalism with elements typical of Impressionism.
Late Period
In his late period, Liebermann continued to evolve, both personally and artistically, often focusing on more personal subjects. He settled back in Berlin and became one of the leading figures in German art, particularly as a proponent of Impressionism.

Legacy
Liebermann left a significant imprint on the world of art. He founded the Berlin Secession, a group that was crucial in promoting modern art in Germany. His legacy is also tied to his impressive collection of French Impressionist works.
Liebermann’s influence extended beyond Germany’s borders, shaping the broader continental European Impressionist movement.
Personal Life and Sociopolitical Context
Max Liebermann’s personal life and his interaction with the sociopolitical milieu of his time were heavily influenced by his Jewish heritage and his position in the Berlin bourgeoisie. As an acclaimed artist, he navigated the shifting political landscape of Germany with a relationship to figures like Albert Einstein and across varying political regimes.

Family and Personal Relationships
Born into prosperity, Max Liebermann was the son of a successful Jewish banker and manufacturer, which positioned him within the affluent circles of Berlin’s bourgeoisie. He was married, but information about his marriage and private relationships remains less documented in typical historical records. This connection to the bourgeoisie and Jewish cosmopolitanism would later influence both his artistic perspective and social interactions.
Liebermann’s social network included numerous intellectuals and artists of his time, reflecting a confluence of cultural and intellectual richness. His association with prominent figures such as Albert Einstein underscores the mingling of scientific and artistic advancements in his social sphere.
Engagement With Politics
Throughout his lifetime, Liebermann witnessed the factors that shaped modern Germany – from the rule of Paul von Hindenburg to the rise of conservative movements. Although not a vociferous political actor, the painter’s life was inevitably intertwined with the political upheaval of his era, including the profound impact of anti-Semitism. The rise of anti-Semitic sentiments within Germany, particularly in the arts, rendered his position increasingly complicated and contentious. Despite his standing and contributions to German culture, Liebermann and his work were not immune to the prejudices and political shifts that intensified with the growth of anti-Semitic policies.

Liebermann’s life in Berlin served as a front-row seat to the contradictions of his time: the vibrancy of the cultural capital against the backdrop of changing and often volatile political ideologies. His identity as a member of the Jewish community and as a respected figure in the arts meant that he both contributed to and was subject to the complex layers of socio-political dynamics of early 20th-century Germany.
Artistic Career and Influences
Max Liebermann’s career was a fusion of Realism and Impressionism, marked by his role in the Berlin Secession and his profound influence on German art. His encounters with French Impressionists and studies in Paris shaped his techniques and use of color.
This lead to significant contributions to the German Impressionist movement.
Impressionist Transformation
Liebermann’s early exposure to art came through his study of painting in Weimar, Paris, and the Netherlands. It was in Paris where he discovered Impressionism, captivated by the innovative works of Édouard Manet and Degas. Far from the confines of academic art, he embraced the Impressionist focus on light, momentary impressions, and everyday subjects.
- Main influences: French Impressionists
- Techniques adopted: Emphasis on light effects, loose brushwork, depiction of movement
- Shift in style: From Academic Realism to Impressionist sensibilities

Berlin Secession and Leadership
A pivotal moment in Liebermann’s career was his pivotal role in founding the Berlin Secession in 1898. Breaking away from the conservative Prussian Academy of Arts, Liebermann and his contemporaries fostered a progressive art community in Germany.
As the Berlin Secession’s first president, he became a leader and advocate for German Impressionism, driving the movement forward.
Key Artworks and Techniques
Liebermann mastered a wide range of subjects including self-portraits, rural scenes, and everyday life. His key artworks reflect a consistent evolution in style and technique, mirroring the essence of Impressionism. The artist’s deft use of color and texture brought German daily life to the canvas, often composed with a printmaker’s eye for detail.
- Subject variety: Self-portraits, rural and urban life
- Stylistic evolution: From detailed Realism to dynamic, color-rich Impressionist techniques
- Printmaking: Produced fine prints, further showcasing his versatility and skill
Through brushwork, an expert palette, and a gifted insight into the world around him, Max Liebermann solidified his place as a luminary in German Impressionism.

Legacy and Memorials
Max Liebermann’s impact on art extends beyond his prolific body of work, with memorials and societies dedicated to preserving his legacy and recognizing his contributions in Germany and beyond. Throughout his lifetime and posthumously, Max Liebermann received multiple accolades for his contributions to art. Significantly, he was honored with the title of Honorary Citizen of Berlin.
This recognition highlighted his influential role during the Weimar Republic, reflecting his importance not only as an artist but as a cultural figure in German society.
Liebermann Villa and Max Liebermann Society
- Liebermann Villa: The artist’s summer home on the Wannsee in Berlin is now a museum known as the Liebermann Villa. This location preserves his artistic environment and provides public access to his life’s work and personal history.
- Max Liebermann Society: Established to perpetuate his legacy, the society aims to foster appreciation for his role in modern art. The society is dedicated to the study and promotion of Liebermann’s work, reflecting his artistic journey and impact, which was strongly influenced by his experiences in France and his German heritage.

Max Liebermann’s artistic legacy stands as a testament to his mastery of capturing the essence of life through his paintings and prints. His unique blend of Impressionist and Realist techniques, coupled with his profound understanding of human emotion and the beauty of the everyday, has left an indelible mark on the art world. Liebermann’s ability to evoke a sense of timelessness in his works continues to resonate with audiences, solidifying his place as a revered figure in German art history and a source of inspiration for generations of artists to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Artistic Movement Is Max Liebermann Associated With?
Max Liebermann is closely associated with Impressionism. He was one of the main proponents of this movement in Germany, drawing on techniques of French Impressionists and the Dutch Hague School.
Which Notable Works Did Max Liebermann Create?
He created numerous naturalistic studies highlighting the life of the poor. Some of his notable works include The Bleaching Ground, Flax Barn at Laren, and The Basket Weavers.
How Did Max Liebermann Contribute to the Development of Modern Art?
Liebermann contributed to modern art by embracing Impressionistic techniques, which broke away from academic German art traditions. He also played a pivotal role in founding the Berlin Secession, an influential avant-garde movement that provided a platform for modern artists.
Isabella studied at the University of Cape Town in South Africa and graduated with a Bachelor of Arts majoring in English Literature & Language and Psychology. Throughout her undergraduate years, she took Art History as an additional subject and absolutely loved it. Building on from her art history knowledge that began in high school, art has always been a particular area of fascination for her. From learning about artworks previously unknown to her, or sharpening her existing understanding of specific works, the ability to continue learning within this interesting sphere excites her greatly.
Her focal points of interest in art history encompass profiling specific artists and art movements, as it is these areas where she is able to really dig deep into the rich narrative of the art world. Additionally, she particularly enjoys exploring the different artistic styles of the 20th century, as well as the important impact that female artists have had on the development of art history.
Learn more about Isabella Meyer and the Art in Context Team.
Cite this Article
Isabella, Meyer, “Max Liebermann – Discover the Founding German Impressionist.” Art in Context. March 19, 2024. URL: https://artincontext.org/max-liebermann/
Meyer, I. (2024, 19 March). Max Liebermann – Discover the Founding German Impressionist. Art in Context. https://artincontext.org/max-liebermann/
Meyer, Isabella. “Max Liebermann – Discover the Founding German Impressionist.” Art in Context, March 19, 2024. https://artincontext.org/max-liebermann/.